Product-market fit: how to find and measure it
Oct 26th, 2021

Contents
What is a product-market fit?
How to find a product-market fit?
Product-market fit metrics and measuring
Product-market fit examples
Feedback and improvements
The lack of market need is the main reason for startup failure. Product-market fit is one of the most crucial elements needed to create a successful business. It indicates that people are interested in the company’s product and are willing to pay for it because the offering is better than the other alternatives. Due to this reason, finding a product-market fit should be among the first and foremost objectives for your business.
Snapchat is an excellent example of a startup that managed to find product-market fit. This resulted in more than 293 million daily active users and $2.5 billion in annual revenue since its initial launch in 2011. In 2012 Snapchat users were sharing over 20 million images per day or about 231 per second. 10 million Instagram users, in contrast, were sharing only 25 photos every second. During the early stage, the target audience of the startup consisted of bloggers and students. Snapchat quickly became popular at colleges and high schools through word of mouth. The company was gathering customer feedback and constantly improving the application, which was important in reaching product-market fit.
Let us take a closer look at the concept of the product-market fit and the practical steps required to achieve it.
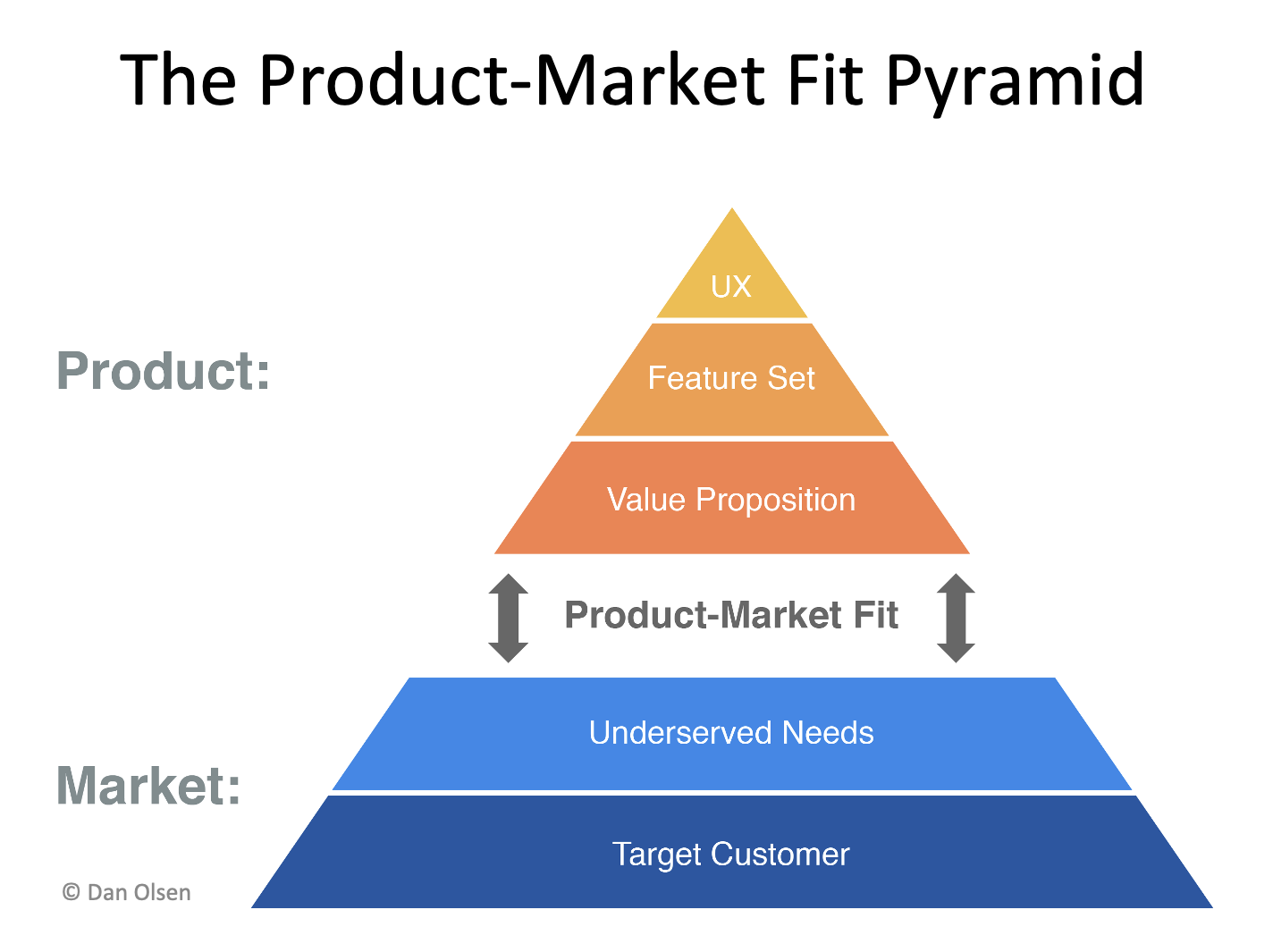
Source: Dan Olsen's The Lean Product Playbook
What is a product-market fit?
Product-market fit is the degree to which the product meets the target consumers’ needs and fulfills the market demand. PMF occurs when the business owner develops a solution that fills a certain market niche and evokes the desire to buy it. Product-market fit is not a constant state. Instead, it can be described as the continuous process of adjusting to changing client needs.
The term was coined by the co-founder of Benchmark Capital, Andy Rachleff, and later popularized by entrepreneur Mark Andreessen, the co-founder of Andreessen Horowitz. Rachleff’s idea was based on the study of the investing approach of Dan Valentine, venture capitalist and founder of Sequoia Capital. Andy Rachleff explains product-market fit as a combination of “the feature set you need to build, the audience that’s likely to care, and the business model required to entice a customer to buy your product.” Marc Andreessen defines it as “being in a good market with a product that can satisfy that market.”
The alternative definition by Dan Olsen, the author of “The Lean Product Playbook”, says that the product-market is “meeting the underserved needs of target customers better than the competition”. Thus, we can summarize that product-market fit refers to the situation when the company provides value for a substantial number of customers who perceive the value with the effective delivery method, and differentiates itself from the competing companies.
How to find a product-market fit?
The process of achieving a product-market fit differs for each company. Therefore, to create an outstanding product, you need to understand the problems your solution addresses and the issues your clients are trying to overcome with its help. So, the goal of finding product-market fit should be number one on your company’s priority list as it would dramatically increase the chances of business success. Despite the fact that the path to product-market fit is unique for each business, you can find it by focusing on the key areas and following several simple steps we will discuss below.
Step 1. Determine your target audience
The first step in developing your product-market fit is to determine the target customers. They will represent the users who decide how well the product aligns with market requirements. The next task is to use market segmentation to later target customers more effectively by relying on their unique features, improving marketing campaigns and discovering more opportunities. Then you need to create buyer personas to ensure that your team’s efforts are tailored to your customers’ needs. Therefore, the main objectives of this step are to analyze your product or service, conduct a competitive analysis, segment your target market into several types of customers, and perform research.
Step 2. Talk to your customers
Gather feedback from your customers to identify their underserved needs and discover a suitable market opportunity. Determine the common challenges they face and how much they are willing to pay for you to solve their problems. The competition plays a huge role in the degree to which the product fits customer demands as they evaluate the solution in comparison to the alternatives.
If you want to improve the existing product, collect data from your sales and marketing departments to understand the recurring complaints. Face-to-face interviews are more effective than online surveys as they provide more useful information.
Step 3. Define your value proposition
The value proposition is the most crucial aspect of your marketing message. It explains why your customers should purchase your company’s products instead of the competitors. A great value proposition is clear and understandable. The statement should be relevant to the target audience. Describe how your solution addresses customer problems and provide the set of advantages. To define your value proposition, you need to determine customers’ pain points, identify your product’s benefits, describe what value your solution adds to the market, connect it with the problems and make it unique.
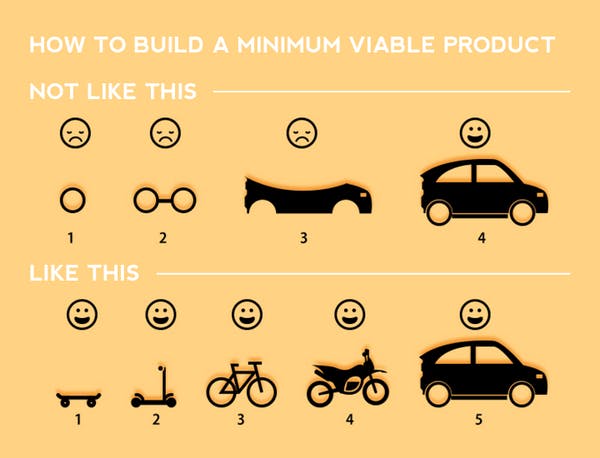
Step 4. Specify your MVP feature set
The following step is to define the features that your minimum viable product will include. If you add sufficient functionality to your product, you will be able to demonstrate the value to your customers, save time and money and leave space for improvement. MVP will help you determine the features your solution lacks or what can be done better. Moreover, you might understand that the customers will not use the specific function, so you can remove it. The primary objective is to continue adjusting the minimum viable product feature set until the potential customers approve it.
Step 5. Design your MVP
Once you have determined the MVP feature set, it is time to create the test version of your product, so your customers can provide feedback and valuable insights. Building the MVP prototype usually takes less time and effort than producing the working version of the minimum viable product. The prototype will brilliantly represent your product without the need to build it.
Step 6. Test your MVP with customers and analyze feedback
The last step is to test the MVP prototype with target customers. The goal of MVP testing is to receive feedback from the audience, make improvements to the product and determine whether the idea is valid or not. The most efficient method of MVP testing is user interviews. First, provide the list of the problems your solution aims to solve and put open-ended questions to your customers. Then ask them to rank the issues and analyze their level of interest. Finally, present the MVP as the solution to the problem and offer people to try it. The other way to test your minimum viable product is to create a landing page demonstrating its features or promote the solution through advertising. This will help you to understand whether your MVP interests the target market. You can also test the prototype on crowdsourcing platforms. If the users like your idea, they would be willing to invest in the development of your product, so this would be the perfect indicator of the product-market fit.
After conducting tests:
- analyze the received feedback,
- identify similar answers and pay attention to common patterns,
- use the information received from the customers to modify the initial prototype and address consumer issues.
You might learn that a majority of your audience consider themselves too young or too old for your product. Then you can ask the respondents who they assume the product is intended for. The feedback will reveal how your product is perceived in the market. You might understand that your solution is more niche-oriented than you expected. In this situation, you need to return to step 1, review your customer profiles, and proceed from there.
If the product is not right, but the audience is a fit, return to step 2 and gather feedback to understand what adjustments your customers would apply to your product to make it more appealing. Then, move to steps 3 and 4 to review your value proposition and minimum viable product features.
Netflix is a company that constantly adapts to changes, monitors trends and shifts in the market, and takes advantage of them. Netflix changed its business model multiple times, adjusting to user demand. In the early 2000s, Netflix achieved the product-market fit when the company positioned itself as the alternative to traditional DVD rental stores. Netflix started shipping DVDs by mail as part of its membership services and allowed clients to keep videotapes for an unlimited period of time. Later, when the DVD trend faded, the company turned into a subscription-based streaming platform and reached product-market fit owing to cheaper and better services.
Step 7. Build the product and take it to the market
Prepare a product launch plan and create a marketing strategy to take advantage of the opportunity to promote your offering. The product launch event has a significant influence on market acceptance. It helps inform the clients that the product is available for purchase and introduces the solution to the market. With product launch, you will gather valuable information from early users, build anticipation and brand awareness. Create content that will align with marketing activities, such as landing pages, blog posts, and product tutorials.
Step 8. Improve product-market fit as you scale
Keep reviewing your product after it is launched. Take small risks and redesign the product in accordance with the customer base, competition, and the new needs of target audiences. Remove the elements that do not work, experiment with new functionality, and test the features on a small scale. Analyze qualitative and quantitative metrics, conduct customer surveys to adapt to changing market conditions, and stay ahead of the competition.
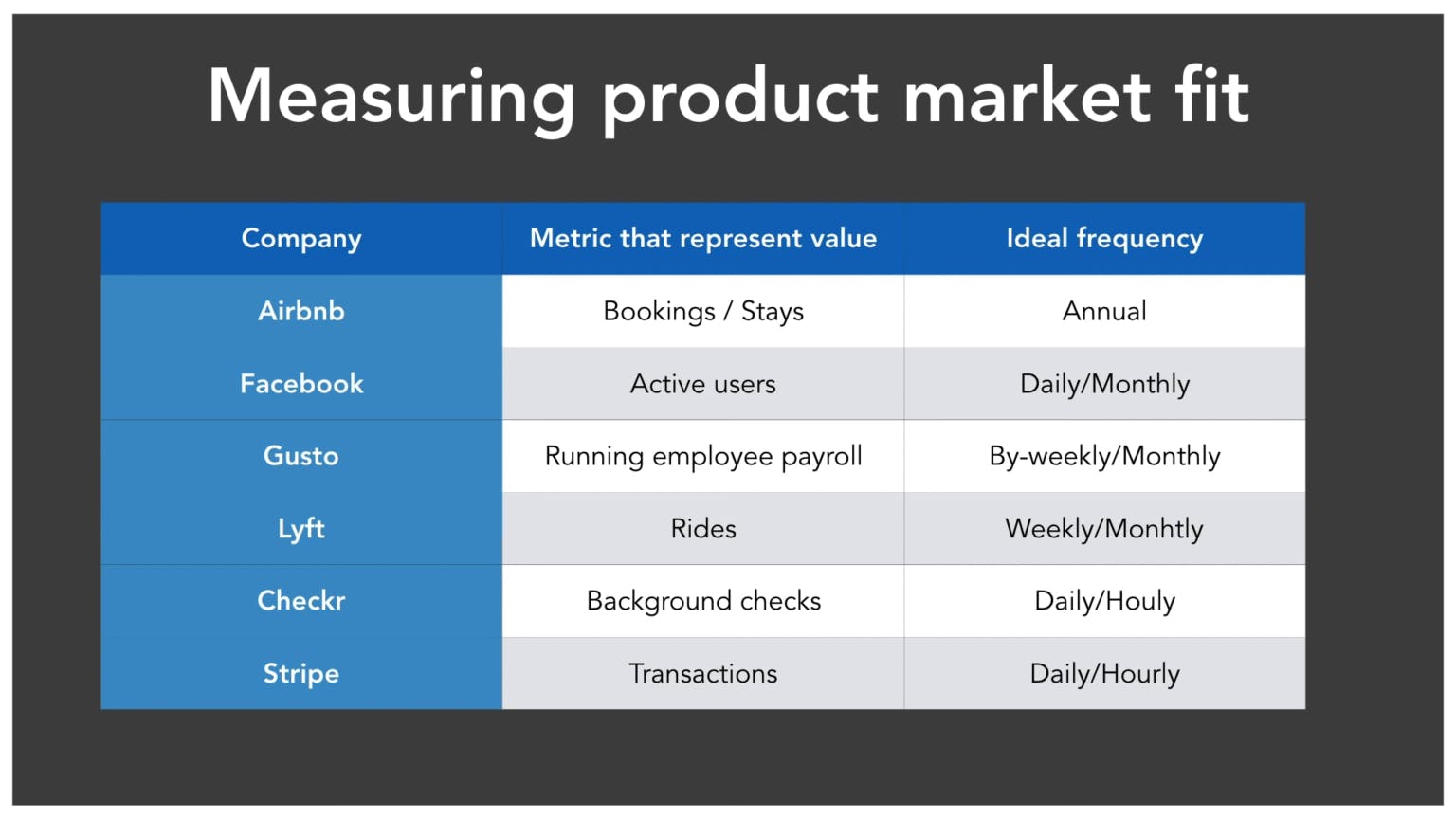
Product-market fit metrics and measuring
There are several quantitative metrics that will determine the percentage of customers who consider your solution as a ‘must-have’. We will discuss them further in greater detail.
Growth rate
The growth rate will provide you with crucial information about your company’s performance over time. It is one of the essential metrics the investors examine before deciding whether to fund the company or not. To measure the product-market fit, you can analyze the growth in the number of users or revenue. The formula for calculating the monthly or annual growth rates is as follows:
Growth rate = (Period 2 – Period 1) / Period 1 * 100
It is important to note that a high growth rate does not necessarily mean that you have achieved product-market fit (as it can be followed by a similarly high churn rate). Thus, you need to pay attention to various factors that may have led to this and take into account other metrics. In some cases, high growth rates can result from marketing activities and do not represent product-market fit.
Churn rate
The churn rate is the number of customers who stop using your product over a certain time frame. With this metric, you can understand whether people are interested in your product or not. The churn rate varies depending on the type of business and its specifics. Newly established companies usually have higher churn rates compared to organizations that have been on the market for a longer time. You should inspect your monthly and annual churn rates to have a clear picture of your progress. The churn rate formula is:
Churn Rate = (Lost Customers ÷ Total Customers at the Start of Time Period) x 100
Net promoter score
The net promoter score is a scale that ranges from -100 to 100. With this metric, you can estimate customers’ willingness to recommend your company’s products to other people. To calculate the net promoter score, you need to ask your customers a key question: “On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend the product to a friend or a colleague?” Then the respondents are categorized into three main groups depending on the answer: promoters, passives, and detractors. Finally, you want to subtract the percentage of detractors from the percentage of promoters. The final number will show you whether customers generally enjoy using your product. You may compare it to similar metrics in your industry and review it regularly to see if the satisfaction rate is improving.
Product-market fit examples
Now we will look at three successful companies that began their journey as startups but turned into global enterprises with a multi-million customer audience. We will consider how these companies managed to find their product-market fit and adapted to evolving market needs.
Spotify
The idea to create Spotify appeared after Napster’s collapse, and the sales plunge in the music industry as the users started downloading albums from illegal sources. Spotify’s founder Daniel Ek suggested the listeners the opportunity to consume high-quality music legally for a small fee. Now the platform has over 365 million active users.
The startup was created at the most opportune time when the other elements of product-market fit already existed. There was a target market with music listeners, distribution channels, and a lot of content. The platform provided consumers a way to listen to music without addressing any legal issues, resulting in a 20-30% annual growth rate.
Slack
Slack is a well-known messaging platform for business communication. Despite the fact that now Slack’s target customers are mostly enterprises, the company paved the way to product-market fit by targeting individual users. Between March 2020 and April 2021, Slack generated $902 million in revenue, but it all began with a startup that did not even have a sales team.
At first, Slack’s founders were developing a role-playing video game. The messaging app was originally intended as a tool for internal communication. However, the team later realized that the solution perfectly fits into a free niche, while there are already many role-playing games on the market. The decision to give up the original idea in favor of better opportunity has brought over 12 million users by the end of 2020.
In the early years, Google had a lot of competitors in the market. At that time, the search engines were making a profit from selling the advertising space next to search results. In 2003, Google leaders decided to introduce AdSense. This was a totally new concept that allowed to display the advertisements beyond the search page results. The technology analyzed the web pages and automatically displayed the relevant advertisements.
Google discovered a gap in the market that no other search engine could fill and satisfied that need. In 2017, the annual revenue from AdSense amounted to $95 billion.
Feedback and improvements
Make whatever adjustments are necessary to achieve product-market fit. Improve your product, move to different markets, change your team, name, and overall vision. This was the path to the success of the world-renowned companies. Oftentimes, they drastically altered their initial strategies to find product-market fit and later reimagine it as the company grew. And it worked!
Once your company reaches PMF, the next steps are to grow your business and listen to customer feedback to improve the fit. By surveying target customers and gaining valuable insights, you will increase your chances of creating outstanding products.
