Product marketing: the definitive guide
Jul 14th, 2021

Contents
What is product marketing?
Product marketing strategies and activities
Product marketing manager and product marketing team
Conclusion
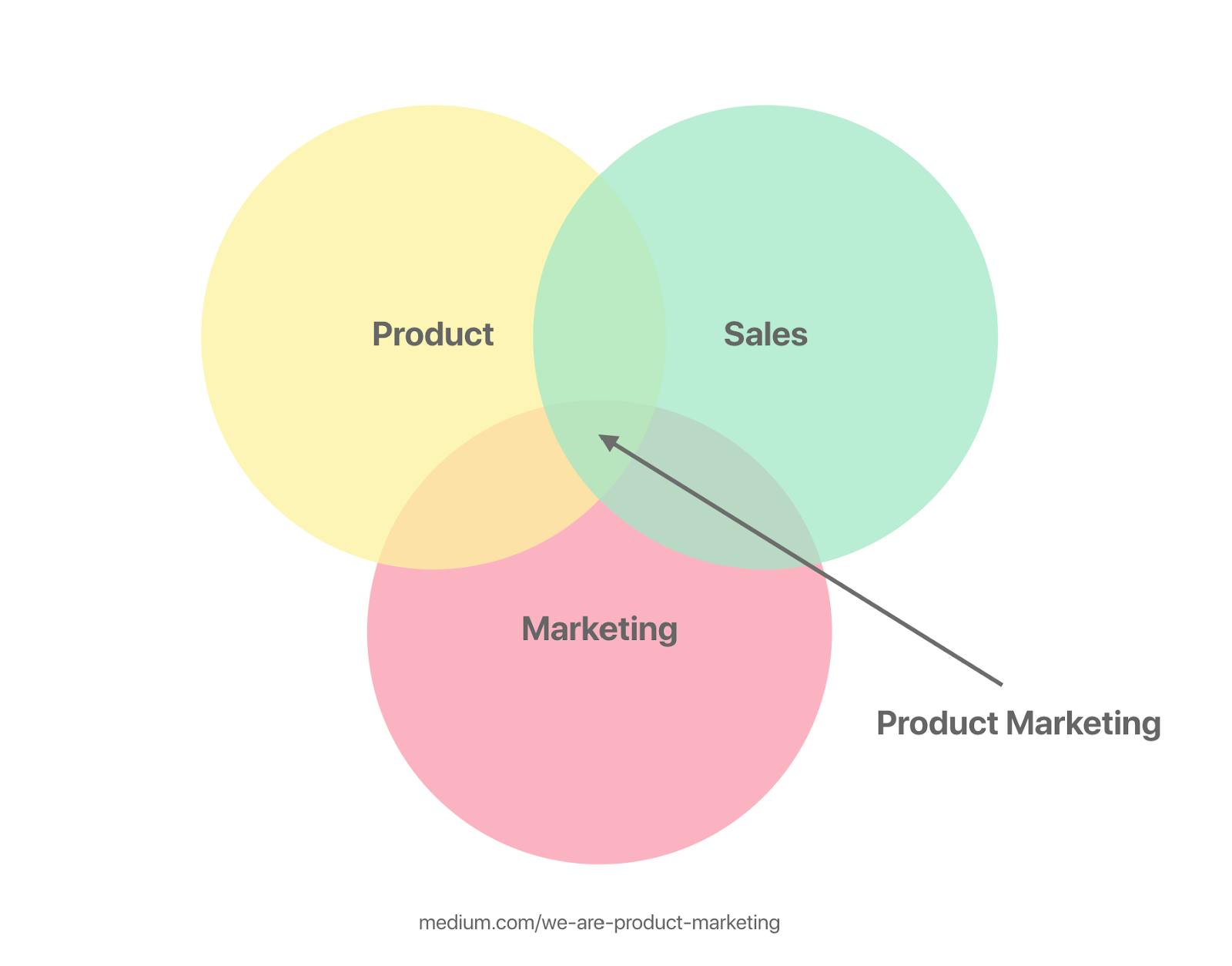
Outstanding product marketing evokes a feeling of excitement about the product and gives customers a reason to purchase it. Customers and internal teams get an understanding of the product’s unique value and what differentiates it from the competition. Product marketing determines customer pain points and focuses on the ways the product can solve their problems. It lies at the intersection of marketing, sales, and product management.
Source: Paul Connor
Behind every successful product, there is excellent product marketing. New Balance is a global $4 billion company operating in more than 120 countries worldwide. The brand managed to achieve recognition due to the strong connection with the audience and the unique fit into its market niche of stylish everyday and athletic shoes. The additional challenge was the severe competition in the sneakers market with the opponents like Nike, Under Armour, and Adidas. New Balance has succeeded thanks to the differentiated position. Instead of selling sneakers, the brand is “reinventing how athletic looks”.
What is product marketing?
Product marketing is a process of introducing a new product to the market, identifying its target audience, and promoting the product to the end-users, prospects, and customers. Product marketing focuses on creating positioning, differentiation, and messaging and ensures that the sales team collaborates with the marketing department to achieve product success.
The responsibilities of product marketers usually include buyer persona development, creating positioning and communication that attracts prospects and customers, formulating the go-to-market strategy and the plans for product promotion and distribution. The other tasks usually performed by product marketers are managing product launch, content marketing, storytelling, and website management.
Product marketing is responsible for three main steps in the customer funnel: acquisition, engagement, and retention. The first step requires advertising to build awareness about the product or service. The second step is to ensure that people who learn about the product end up purchasing it. The final step is to retain the prospects converting them into satisfied and returning customers.
The main difference between product marketing and the other branches of marketing is the focus on the specific products or product lines rather than specializing in promoting the overall company or brand name.
Product marketing vs product management
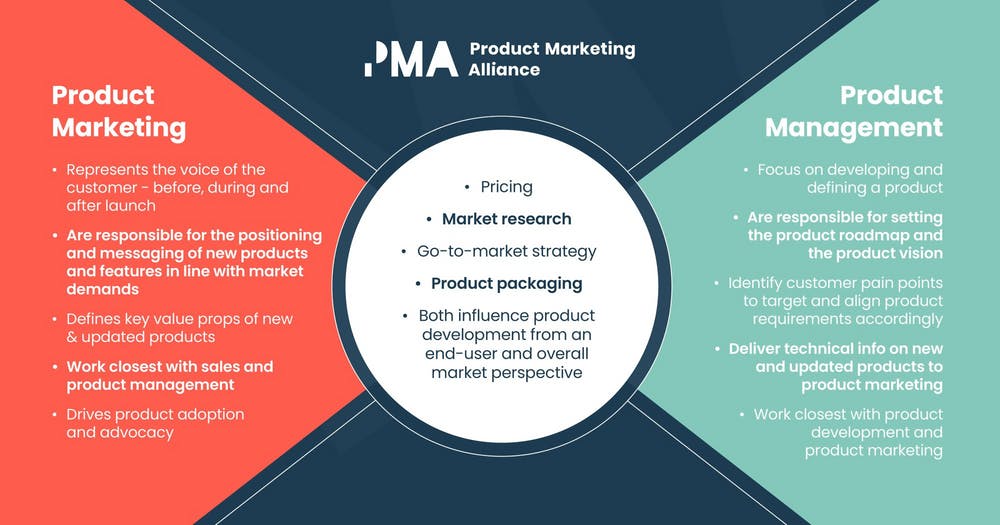
Product marketing and product management have different functions despite a common misperception about the similarity of the processes. The role of a product manager is to develop and define a product, while the responsibility of the product marketer is to get the product to the market and place it in front of the potential customer, on the shelf of the supermarket, or the screen of their phone or laptop.
Source: Product Marketing Alliance
Product management strives to understand the market needs, implement product strategies and maintain product alignment across company teams and departments. Product marketing is also concerned with identifying the demand and consumer needs. However, it puts emphasis on learning about the buyer of the company’s products. In short, product managers’ scope of responsibilities is to create value. The product marketer, in turn, focuses on communicating the product value.
Product marketing strategies and activities
The product marketing process is divided into four stages which we will discuss in detail below.
Stage 1. Product growth strategy and roadmap
Product roadmap planning. The first step involves creating the product roadmap together with the product management team. Product roadmap is the visual of your product’s evolution over time. This strategic document highlights essential points and typical stages of product development. It communicates what problems the product solves, how it addresses these issues, who faces the problem, and what differentiates the product from the competitors. In this case, the product manager plays the role of the connecting link between the roadmap and the other departments of the organization.
Cooperation with engineering and product management teams. In the initial stage of product development, marketers apply the existing information about the market and consumers to make future changes to the product roadmap. It is critical to maintain good relations between different functions in the organization, including engineering and tech teams, product management, and product marketing, to make well-informed business decisions.
Customer validation. This step usually takes place simultaneously with engineering and, in some cases, prior to the complete product roadmap creation. Through conversations with consumers and user or consumer testing activities, the customer validation phase allows predicting the consumers’ reaction to the product even before its development. If you are not aware of the product’s features or functions, you can concentrate on the advantages and value the product should bring to the market.
Planning of the future. The final step of the roadmap planning stage implies developing the company’s strategy for the future. The plan should encompass the vision for the feasible time frame, a look ahead for the coming two-three years of product growth and transformation. In addition to the roadmap, the product marketer creates the customer strategy template, which contains the cross-functional input essential for effective teamwork.
Stage 2. Product market positioning and messaging
Customer and market research. Before working on messaging and positioning, it is crucial to understand the product’s place in the market, the demand, and the target user. At the following stage, product marketers focus on creating the buyer personas and gathering information about the customers’ demographics, motivation, and behavioral patterns. The next step is to identify the competitors, learn about their strengths and weaknesses and perform a competitive analysis. During this stage, the product marketer works in collaboration with product managers, design and analytics departments.
Customer segmentation. At this stage of your marketing strategy, you need to divide the customers into groups according to specific characteristics, such as location, age, buying habits, and hobbies. Dividing the customers into groups will help createmore successful communication campaigns focused on specific needs of different target audiences, which your product can help them solve.
Developing positioning strategy. When the product marketer has enough information about the target audiences and the competitors’ offerings, it is time to develop the positioning. The key steps of this phase are the understanding of the unique features and benefits of the product, defining the positioning statement, and creating the perceptual map.
Messaging. Customer interviews are helpful in developing messaging because they allow for learning what words the target customers use to describe the pain points and expectations. The brilliant marketing message communicates the product’s core value using simple and familiar language and conveying unmistakable meaning that needs no further explanation.
Product marketing brief. As a sum of the previous points, the product marketer creates the positioning document or product marketing brief that contains goals and objectives, positioning, the results of market research, and customer segments.

Source: Marketing & Growth Hacking
Stage 3. Product promotion and customer acquisition
Launch of the product. Once the product marketer developed messaging and positioning, it is time to bring the product to the market. The launch projects can be divided into several categories according to size. For instance, major product launches are advertised through PR and events, minor launches announcing new and improved features via the blog, and incremental launches utilizing newsletters.
Major releases coordination. In case of major launches, it is essential to create a run-of-show document that ensures discipline and alignment. This spreadsheet contains a list of the people who take part in the product launch and their specific duties. The document also has instructions for the contingencies.
Asset creation. Product marketers create the assets in collaboration with marketing and creative departments. Marketing assets include blog articles, advertising, influencer campaigns, launch videos, emails, or events.
Customer acquisition testing. Within this step, the product marketing team tests different ways to promote the product, such as content marketing, organic and paid social media campaigns, organic search marketing, and email marketing. The product marketers make and test various hypotheses to find the most powerful and cost-efficient online and offline methods of acquiring customers.
Sales organization. The product marketing team and sales department are inextricably linked. Product marketers help sales to get a better understanding of the product roadmap. The sales department can provide valuable insights to the product marketing team because they communicate directly with the customers. At this stage, it is vital to understand what information will be required for the sales team to interact with customers and provide the materials with a value proposition.
Beta tests and case studies. This step will be essential for developing the story, learning how to resolve objections, and creating content for the customers. Product marketers typically conduct beta tests to evaluate the messaging and the materials created for the sales department. The collaboration between product marketers and a part of the sales team plays a big role in messaging consistency and strong positioning. The knowledge obtained from this partnership will be helpful in the future during the comprehensive sales team trainings.
Stage 4. Product growth implementation and scaling
During this phase, the focus of attention shifts to more traditional marketing. The role of a product marketer at this stage depends on the size and the structure of the organization. If the product marketer is involved in the overall marketing team, his responsibilities will cover the tasks of the amplification phase. Otherwise, if the product marketer sits with the product team, the responsibility would fall on the existing marketing department. The main objective of this stage is wide-scale customer acquisition and retention, which is tracked using various metrics, such as conversions and sign-ups.
Content creation. Product marketers are responsible for creating various types of content for lead generation and sales enablement. These marketing assets include blog posts, case studies, whitepapers, email templates, presentations, social media messages, and one-pagers.
Advertising and promotion. At this stage, the product marketing team focuses on the most efficient channels that showed the best performance during the testing phase. The marketers also test the new advertising channels to increase the customer base. The acquisition channels might include organic search, email marketing, direct traffic, paid search, referrals, social media, and paid social and events.
Sales enablement. The sales team and product marketers collaborate before, during, and after the product’s release to the general public. Product marketers develop the materials needed for the sales department to close more deals. These might include competitor battle cards, sales scripts and training, win/loss analysis, and pricing calculator.
Product marketing manager and product marketing team
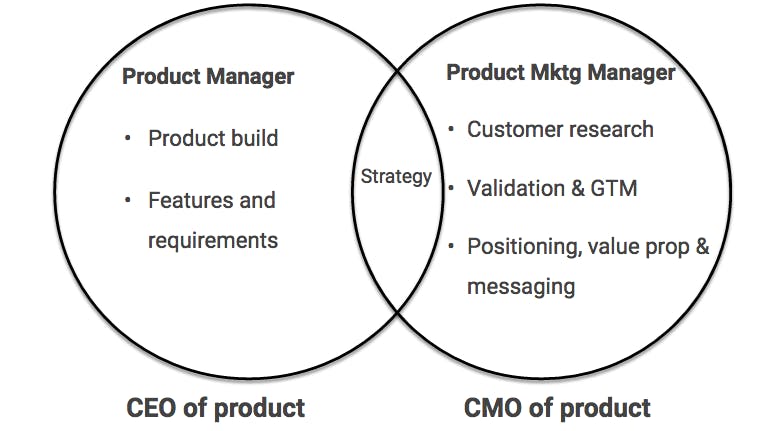
There are two general approaches to organizing the product marketing team – early stage and late stage. The choice of a suitable course depends on various factors, such as the size of the organization, the stage of the business growth, as well as the variety of the products and services. We will consider both of them in detail below.
Source: The Product Launch
Early stage - single product marketing manager or small team
This structure typically implies one or two product marketers working together with the product manager. When the late stage of the organization has multiple product marketers, the workload is usually distributed among the specialists. If the company has a small product management team, the product marketer is a generalist who takes responsibility for all areas of product marketing within the company.
According to this approach, product marketer’s tasks include a full spectrum of activities, such as developing buyer personas, identifying the pain points of user personas, creating messaging and positioning, collaborating with the sales and design teams, and conducting the analysis of the new and existing products. If the company sells the portfolio of the products, the product marketer would be responsible for all of them.
In this structure product marketers focus on a larger number of success metrics than their colleagues from enterprises with a dedicated product marketing team. The product marketer will monitor both company metrics, such as average customer lifetime value, and user metrics, such as the number of trial downloads.
Late stage - product marketing team
According to the second approach, there are some standard roles and responsibilities within a large product marketing team. At the late stage, the product marketing department typically includes the head of product marketing, multiple product marketing managers responsible for different products or services, content marketing manager, paid-ads specialists, copywriters, designers, sales enablement content specialists, and others depending on the specific marketing tactics the company is using.
In this mode, the product marketers are usually involved in tracking competitor activities and monitoring industry trends and thought leaders. For that purpose, product managers often partner with analysts. The sales enablement specialists’ objective is to help the sales team reach their highest potential, so they collaborate with the sales department to develop training and sales collateral and enhance the team’s total win rate.
The group of content enablement specialists focuses on developing product landing pages, sales decks, one-pagers, and other marketing materials. The roles are assigned according to the product or service or the company’s internal departments. If the company frequently launches a new product or feature, it would have the product marketer responsible entirely for the product launches.
Conclusion
Product marketing is the unique sector that affects every department of the company, including sales, customer success, and product. The primary role of the product marketer is to develop a positioning that highlights the core value of the product or service. The specialist is also in charge of creating a messaging strategy that would increase customer awareness and product adoption on the market.
Positioning and messaging are the key elements that help the organization to remain competitive within the industry and differentiate its products from the other offers in the market. Thus, the product marketers’ functions are of major importance for every company’s overall success.
