Product positioning: definition, strategies, maps and examples
Apr 1st, 2021

Contents
What is product positioning?
Product positioning strategies
Perceptual product positioning map
Product positioning process
Product positioning examples
Product positioning plays a crucial part in your overall marketing strategy. Positioning allows focusing on the specific niche, target audience, or idea. With the help of positioning, your product or service can stand out in the competitive market.
Apple is an example of outstanding product positioning. The company emphasizes product quality and performance. In some cases, Apple delays shipments to deliver truly high-quality products rather than sell more gadgets. This approach helped the tech giant build customers’ loyalty and trust.
What is product positioning?
Product positioning is a process of communicating the benefits of your product to the target audience. Positioning defines what place a product or service occupies in customers’ minds and how it differs from competitors. The process is related to identifying the appropriate market niche for the product and getting it established in that area.
In simple words, within the process of positioning, the marketers determine the group of customers with common characteristics. Then they analyze the product’s strengths and weaknesses and compare it to their competitors’ offerings. For example, Bentley positions its products as symbols of luxury. Apple presents its operating systems as innovative and user-friendly products. In the advertising campaigns, Starbucks describes the beverages using the following characteristics: “the best coffee”, “the finest milk”, “clean and natural”, “rich and smooth flavors”, “100% recycled paper use��”.
Superb positioning has a wide range of benefits. It makes the product distinctive and helps communicate its unique selling proposition. Product positioning broadcasts a distinct image of a product or service, influencing how consumers perceive the product relative to the competitors.
Product positioning strategies
There are several approaches to present your product in the most favorable light. You can stick to one strategy or use multiple methods simultaneously. The strategies take into account different aspects, such as competition, type of customers, or product characteristics.
Unique product value and characteristics
This type of positioning is based on the product features, quality, or certain distinct value for consumers. The marketers make emphasis on the brand’s durability, safety, reliability, and style. For example, the M&M's chocolate candies tagline is “Melts in your mouth, not in your hands”. The statement highlights the competitive advantage, single product attribute, and clear benefit to the customer.
Focusing on product characteristics can yield positive results, especially if you show the customers what advantages they will receive by using your product.
Positioning in relation to competitors
The brand can apply this type of positioning in relation to or against one or more well-known competitors. The positioning strategy is based on the comparison and acknowledgment of similar features. However, the emphasis is made on the advantages that distinguish your brand from other market offerings.
Positioning with respect to competitors is an effective strategy due to a few major reasons. The first reason is the established image of the competitor’s product. The second reason is the customers’ belief that your product is better than the competitor’s offering.
An example of product positioning against competitors can be seen in an ad campaign by the American soda brand 7-Up: �“7-Up Is The Un-Cola”.

Price and quality trade-off
This positioning strategy focuses on the price-quality relationship and how your customers perceive the product value. More expensive products are often associated with higher quality, while the lower price will position for affordability.
Higher prices allow brands to present the products as exclusive offerings for the top customer segments. For example, such car makers as Mercedes and BMW set higher prices for their products. Still, consumers are ready to pay a considerable amount of money for perfect quality and an extensive set of premium features.
The price-quality approach is an effective positioning tool; however, it is essential to remember that market changes might affect your approach to pricing strategy.
Focus on customer needs and use-cases
Product use positioning is based on the product application and functioning. This type of positioning is created in accordance with the customers’ needs and goals. The positioning-by-use strategy is often applied when a brand reaches for a larger target market or repositions the product to access a different customer type.
Some products on the market have multiple applications. Examples of such products can be scissors and blades. They are positioned accordingly to their uses. The malted milk drink Horlicks was developed for medical use. However, the brand positioned the product as a health drink and expanded the target customer base from medical to retail.
Product category positioning
Product category positioning is based on informing the consumers about the purpose of a product. For example, positioning the product in the wine category creates an association with an excellent complement to dinner, and it also contributes to social relations. It means that asking someone to have a glass of wine is an invitation to meet and socialize. So, the link between the category and the product leads consumers to believe that they would achieve the goal by using the brand.
When the customers are not familiar with the product category, marketers use the points of parity. The points of parity inform people about the goal achieved by using the product with the help of associations. For instance, a coffee brand can be positioned as a product, which would help you feel more energized in the morning. It can also relate to drinking coffee with friends as a great way to pass the time and facilitate social interactions.
As soon as a new product is introduced, consumers try to classify it and define the goal that the product helps achieve. Before the product launch, it is essential to inform the customers what advantages it has over the competitors’ products. That is, why your coffee brand will energize better than competitors or why your wine will be a better pairing for dinner.
Association with cultural and social symbols
Positioning based on cultural symbols takes into account the values and ideas existing in the target market. If customers in the new market are not familiar with the brand, association with cultural and social symbols can cause high levels of awareness.
Within the positioning process, marketers establish the correlation between the brand image and the cultural values that characterize the target market. You need to identify the cultural elements that would fit your brand’s overall image and then add or drop some additional features.
For example, due to Coca-Cola’s marketing efforts, people all over the world draw the parallel between the illuminated lorries with the company’s logo and Christmas holidays. The tradition started with the seasonal advertising campaign more than 20 years ago.
Product customer group or personality
Within this strategy, product positioning focuses on the niche audience or group of customers with specific needs that the offered products can meet. Product positioning by the user suggests that the product is the perfect solution for a particular consumer type. In some cases, the product even contributes to the customer’s self-identity.
For example, Procter & Gamble effectively uses the positioning based on targeted campaigns and niche audiences for each brand. The company created 350 personas for niche campaigns, including first-time washing machine owners, first-time moms, and millennial professionals.
These are the different approaches one can use to position the same product. These strategies are extremely useful when a product has distinctive features that set it apart from the competitors. In case your product is similar to the already existing ones, the marketing experts offer to create a difference deliberately.
Perceptual product positioning map
No matter the strategy you choose, you need to understand how potential customers would compare your product to other products on the market. One way to visualize your positioning against the competition is to create a perceptual product positioning map.
A product positioning map is a two-dimensional chart with horizontal and vertical axes that represent attributes. The attributes might include quality, price, reliability, size, features, packaging, performance, safety, or other positioning comparison criteria.
A perceptual map is effectively a way to plot your product positioning against the positionings of other market players based on two key characteristics of your choice. Perceptual maps are powerful tools used by companies to develop the positioning strategy, understand consumer behavior, track market trends and identify the market gaps. The goal is to find the niche your product would take in the customers’ minds.
Drawing a perceptual map takes several general steps.
Step 1. Define the target market.
The first step is to define the target market. To determine the boundaries of the market, you need to identify customer needs, choose the region you want to study, and decide whether you will track the specific market segment or the entire market.
Step 2. Select the characteristics.
Then you need to select the characteristics of the products you want to compare. These can be quality and price, functionality and price, healthiness and tastiness, reliability or safety and price, or price and performance. Although the price is often one of the two selected comparison criteria, it does not have to be the one you personally use. Oftentimes, customers would be more sensitive to other selection criteria rather than the price. So, your goal should be to choose the ones, which are particularly relevant for your target base.
Step 3. Make the list of products on the market.
The next step is to research how existing players on the market compare based on these characteristics. Create the scores for the competitors’ products by conducting a survey or holding in-depth interviews. Ask the respondents how they evaluate the offerings of competing brands. Identify top competitors, note their strengths and weaknesses. Then analyze the data and provide each product with a comprehensive score.
Step 4. Plot the position of each company on the map.
Once you have scored each product, you can create the perceptual map and plot the brands. When you complete the map, you will have a good visualization of data to estimate your product’s position.
We will present some examples of perceptual maps below to give a better understanding of a topic.
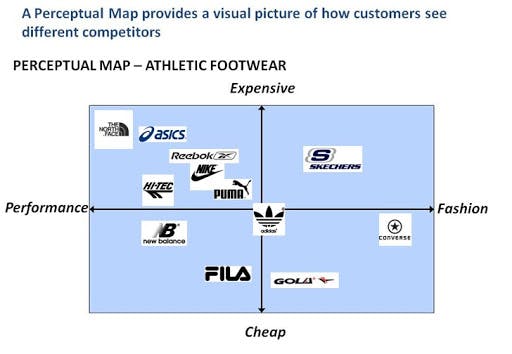
The perceptual map for athletic footwear
The map displays the correlation between the price and performance of the sports shoes. As we can see from the example, the most expensive and functional brands are The North Face, Asics, Reebok, Nike, Puma, and Hi-Tec. New Balance and Fila are cheaper but also suitable for training. Skechers footwear is positioned as a more expensive product, but at the same time, it is more fashionable than the competitors. Gola and Converse are more affordable brands of stylish shoes.
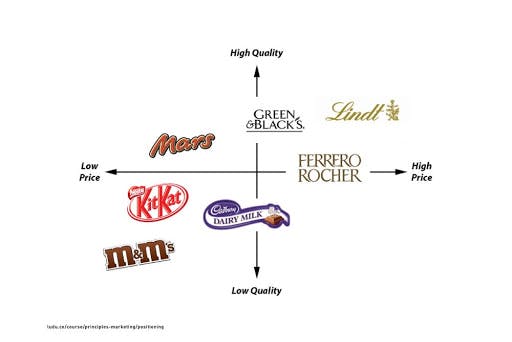
The perceptual map for chocolate manufacturers
The example demonstrates the price-quality ratio and the analysis of the positioning of the most popular chocolate brands. Lindt is the chocolate of the highest quality, and also it is one of the most highly-priced products. Mars and Ferrero Rocher are in the middle of the chart due to the quality attributes. However, Mars is positioned as a more affordable brand. Ferrero Rocher produces more expensive chocolate, but the quality is lower compared to Lindt. KitKat, M&Ms, and Cadbury fill the same market niche according to price and quality parameters.
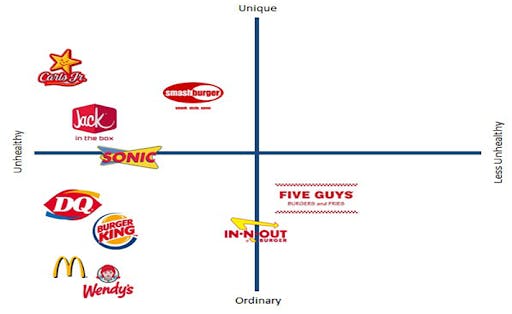
The perceptual map for fast food restaurants
The perceptual map for fast food restaurants analyzes the products according to the criteria of uniqueness and healthiness. According to the map, the healthiest fast food restaurant is Five Guys. McDonald’s, Wendy’s, Burger King, and DQ fall under the category of less healthy and ordinary brands. Fast food restaurants Jack in the Box, Carl’s Jr., and Smash Burger position their products as more unique in comparison to the competitors but less healthy.
Now you are familiar with key strategies and the perceptual map as the primary tool for positioning. Let us discuss the main steps of the product positioning process to help you create an excellent product positioning on the market.
Product positioning process
The positioning process’s objective is to develop an identity that reflects the product’s value and highlights its competitive advantage over the other offerings on the market. The product positioning process usually includes six steps.
Understand the market landscape
The positioning process starts from understanding the target market and market dynamics. You need to define the product or market category to position your product or service. Then think of the target segment and the factors which are important for buyers when they make a purchasing decision. The next step is to understand how the buyers view your competitors in the category.
List your competitive advantages
Сompetitive advantage is a specific feature that allows your product to stand out from the competition. Your product advantage can be the price, features, or benefits. For example, you can offer the products at a lower price than your competitors or develop better characteristics or features, such as personalization, more stylish design, or a quicker delivery. You can also provide unique customer benefits like convenience, time savings, or more choices.
Make a comprehensive list of tangible and intangible benefits that differentiate you from competitors. It is often difficult to maintain a competitive advantage when it comes to features and pricing. Due to this reason, market-leading brands rely on intangible benefits like the feeling of safety or happiness.
Select critical competitive advantages to outline your niche
Once you’ve created a list of all the competitive advantages of your product, it’s time to choose one, which will serve as the backbone of your positioning. The goal is to select a benefit, which is important to your target audience but not used by your competitors. The best tool to perform this task is the perceptual map. A positioning map allows for identifying the gaps on the market and choosing the unique niche that has not been addressed yet.
To create your perceptual map, you need to identify the main attributes of vertical and horizontal axes or the central criteria of your customers’ purchasing decisions. You can have a different view of how your competitors position their products by creating several perceptual maps with additional attributes. Focus on the areas of maps with less competition. This way, you will be able to define your own niche and achieve success by serving it.
Define your positioning strategy
Once you have defined the competitive advantages and niche, it is time to choose one or more appropriate positioning strategies. You can use several strategies at once or target multiple niches. In this case, each niche will require a separate positioning strategy. If you target different niches, you should still focus on one main positioning strategy, while the others will play a supporting role. The positionings should be in line with the primary one and not conflict with each other.
Сommunicate your positioning strategy
The following step of the positioning process is to create the communication plan and deliver your positioning to the audience or audiences chosen within the positioning process. The audience for your communication plan can be employees, investors, customers, or media. Then determine the channels and decide which team members will be responsible for delivering the message.
Maintain and monitor your positioning on the market
The positioning strategy should be designed so that it can easily change according to newly emerging external factors if they affect the customers’ perception of your product. Product positioning is the co-authored experience with customers, so it does not exist in a vacuum and should be revised from time to time. It is important to track the results and analyze the understanding of the market, the product, the benefits, new target markets, and competitors’ achievements.
When there are some changes in the environment or a decline in performance, you need to reposition the product. In this case, you should examine the successes and failures of your previous marketing efforts. Sometimes the companies prefer to launch a new product rather than reposition the existing one because of the high cost.
Product positioning examples
Now when you are familiar with the approach, it is time to look at some exceptional examples.
Hefty
American brand of household products Hefty applies several approaches for positioning the trash bags. The key strategy used by Hefty is positioning by product attributes and features. In its advertising, the company highlights the sustainability and durability of the trash bags. The brand describes the product using the words “ultra strong” and “extra strong”.
The additional positioning strategy is to involve the celebrity. In the case of Hefty, the company invited John Cena to participate in advertising campaigns. The fact that Cena is one of the strongest men in the world is also a reference to the product’s qualities.

Sony
The positioning of LCD TV Bravia by Sony is based on several strategies - the strategy against competitors and positioning according to the product features. In 2006 when the company launched the global campaign, the market of HD TVs was growing, and many brands wanted to take the leading position. People were having trouble deciding what TV to pick, so the main argument influencing decision-making was the price. Sony shifted the focus to the product features - color capabilities.

Head & Shoulders
Head & Shoulders is one of the leading shampoo brands in the world. According to statistics, in 2019 about 7.6 million people in the world used H&S products for men. The company sells 29 million units per year, meaning that about 55 shampoo bottles are being sold every minute.
The key to success was the right choice of the niche market and excellent product positioning. Head & Shoulders is positioned according to the application - as an anti-dandruff shampoo, which clears flakes with one wash. The brand always uses dark-haired men and women with close-up shots of their hair with no dandruff in the commercials. The viewers would be able to see dandruff from such a short distance on such dark hair, and the company uses the visuals to confirm the point that all of it has been washed away. In addition, the brand positions the product as the best in class (positioning against competitors).

Zoom
Zoom Video Communications is a perfect example of an outstanding digital product positioning. The startup is valued at more than $96 billion (as of March 2021), and it has more than 1.7 million daily users. The platform experienced a huge sales boost since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the number of customers continues to grow. The main Zoom’s competitors are the global tech companies such as Microsoft, Cisco, and Google. However, the brand managed to build the perception as The Experts in this niche task (as opposed to Microsoft or Cisco, who offer multiple products for businesses and consumers) and become the number one company in the video conferencing market.
The brand partnered with the other B2B companies to offer their products. While the competitors were positioning themselves using such terms as “conferencing” and “meetings”, Zoom has chosen the other strategy. The brand positioned its product as a part of product-driven startups for conferencing, storage, scheduling, communication, and more. The partnerships with Dropbox and Slack were successful and allowed the company to achieve its goals.

Conclusion
The product positioning process requires choosing the best strategy, drawing the perceptual map, analyzing the market, defining the benefits of your product, selecting and prioritizing market segments, communicating the strategy, and maintaining the positioning over time. When it comes to bringing a product to the market, positioning is the way to learn more about your target customer while finding a way to make a unique statement that’ll relate to them. By knowing how your product’s features meet the consumers’ needs, you have an excellent chance to launch a successful product.
