Value proposition canvas: comprehensive guide with examples
Apr 20th, 2021

Contents
What is a value proposition canvas?
How to fill in a value proposition canvas
Examples of value proposition canvas
When you need value proposition canvas
Value proposition is a clear and concise statement that summarizes measurable benefits your customers will receive when purchasing the products or services. Value proposition motivates the prospective customers to buy from you and differentiates your offering from similar products in the market. It explains how the product solves customers’ problems. Having a value proposition, which is clearly understood and widely accepted by the target audience, gives your company a huge competitive advantage. Thus, the value proposition answers what you offer, the main benefits of the product to your users and why you are the best option.
Value proposition (sometimes referred to as, unique value proposition or UVP) is a vital component of success for any business. It is the basis of your overall marketing strategy and every product or service you create. Value proposition is a great tool to increase brand awareness and loyalty. By creating a value proposition that appeals to target customers’ needs and pain points, you will better understand your audience and convert leads into buyers.
One of the perfect examples of the excellent value proposition is WordPress. The company’s value proposition is “Create a website in minutes”. This statement illustrates the product (free website) and the benefits for the target customers (the opportunity to develop the website or blog very fast).
The other good example is Slack’s value proposition: “Where work happens.” It is targeted at business owners and demonstrates the solution to the problems faced by these people. Value proposition by HubSpot sounds like a simple phrase: “There’s a better way to grow”. This UVP covers the offering and the common goal of the company and the website visitors.
What is a value proposition canvas?
Value proposition canvas is a framework that allows entrepreneurs to establish a product-market fit. It is a tool intended to analyze the relationship between different customer segments and the solutions your business can provide them. The main goal of the value proposition canvas is to shape the product or service to the customers’ requirements.
Swiss business theorist Alexander Osterwalder developed the value proposition canvas in 2014 as a supplement to his Business Model Canvas. During his work on the original framework, Osterwalder understood that people often have difficulties finding the right fit between UVP and customer segments. Value proposition canvas is effective when there is a need to improve the existing product offering or when you want to develop a new offering from scratch. The tool is perfect when you’re working on creating a startup, restructuring the sales process, adding a new feature to the product, and expanding into a new customer segment or new market.
Value proposition canvas structure
Value proposition canvas includes two main elements: the circle responsible for the customer’s profile and the square with a value proposition map. The value proposition canvas template allows for visualizing customers’ needs and defining a response to these needs on one page. It is very convenient to check the match between pains and gains, gain creators, and pain relievers.
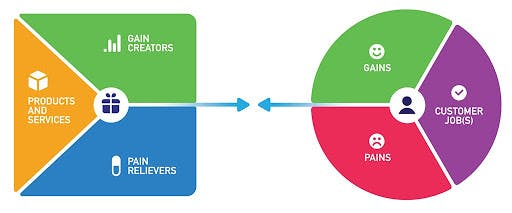
Customer profile
Jobs. This section includes the problems, tasks, and needs your customers are going to meet. There are several types of customer jobs: functional, social, emotional, and supporting.
- Functional jobs are specific tasks your customers want to achieve with your product or service. If you are selling drills, a functional job would be making a hole in the wall to place a new piece of furniture.
- Social jobs are related to the impressions people want to make on others with the help of your product or service. In the case of new clothes, a social job would be to look trendy or get compliments from friends.
- Emotional jobs are related to the feelings the customers want to achieve due to the product. For example, a woman buys some makeup products to feel more confident.
- Supporting jobs are ancillary tasks when the core job is done. There are three main roles: buyer, co-creator, and transferrer. In the buyer’s role, your customer compares offers, stands in the checkout line, or takes delivery of product or service. The co-creator’s role requires posting feedback or reviews or participating in the design of the product. Transferrer’s role implies reselling the product or canceling the subscription.
Pains. These are the difficulties, negative emotions, risks, and undesired situations the customers face before, during, and after getting the job done. The customer pains can include things that the customers find too expensive or time-consuming, make them feel bad, or the obstacles preventing the customers from coming to a decision.
Gains. This segment should contain the benefits, desires, and positive experiences the customers have. Gains often include cost savings or functional utility. It is essential to mention that pains and gains are not polar notions, so they are not necessarily interrelated.
Value proposition map
Products and services. Here you need to mention the products and services which relieve a pain and create a gain for the customer. You can also add various versions of products like standard and premium.
Pain relievers. This section describes how the product or service solves undesired situations, alleviates risks, or reduces negative emotions when your customer gets the job done.
Gain creators. This part of the value proposition map explains the extra value of the product or service, the expected benefits, and how the product would make your customer happier. You can also mention what your product does better than the other offerings in terms of quality, functionality, usability, and other features.
Therefore, value proposition canvas allows you to put yourself in a customer’s shoes and better understand their wishes.
How to fill in a value proposition canvas
Value proposition canvas seems to be quite easy to understand; however, filling it in requires some effort. You need to see your business from the customer’s perspective and go through all possible questions from the target audience. Avoid a common mistake of completing both sides of the canvas simultaneously. Instead, start from the customer’s side of the template.
Uncover customer jobs
Besides the types of the jobs (functional, social, emotional, and supporting), there are other important things to consider, such as the context (place, time, event), observations (past behaviors and decisions), and situational analysis (the anxieties and motives). Examples of customer jobs are eating at a restaurant, attending an event, learning a new skill, buying clothes, choosing a new car, etc.
Here are some key questions to define customer jobs:
- What is the main goal your customer wants to accomplish?
- What are the context and the situation?
- What are the customer’s needs for every stage of getting the job done?
- What are the tasks the customers try to complete in work or personal life?
- What emotional needs does the customer try to fulfill?
List customer pains
Pains are the things that prevent your customer from achieving the goals. There are different types of pains, including internal and external adverse outcomes, risks, and obstacles. Customer pains can be severe or light.
For example, an office worker feels a loss of productivity during the day. He gets interrupted every 11 minutes and it takes about 25 minutes to return the focus on the original task. The solution to this pain would be a mobile application that blocks social media and certain notifications.
As in the case with the jobs, the pains can also be subdivided into functional, social, emotional, and ancillary.
The trigger questions to understand customer pain points are:
- What makes customers feel bad?
- What do your customers find too costly, time-consuming, or demanding significant effort?
- What are the main challenges and difficulties faced by your customer?
- What are the negative social consequences your customers are afraid of?
- What are the financial, technical, or social risks your customers fear?
- What are the common mistakes your customers make?
Describe customer gains
Customer gains are the benefits and positive outcomes expected or desired by the customer. Depending on the gains’ overall significance, they can be distinguished into minimum requirements, the basics, desired gains, and unexpected benefits. Some gains are more preferred than others. For example, the gains can include feeling like a valued team member or saving costs on electricity bills.
The main questions you need to ask to define gains include:
- Which savings would make your customers feel better?
- What would make your customers’ lives and jobs easier?
- What quality levels do they expect?
- How do your customers estimate success and failure?
- What do they dream about?
- What are the positive social consequences they want?
- What features do the customers expect from your product or service?
Define your offering
The next step is to focus on the left side of the canvas and outline the products and services you offer. You have already listed the problems in the customer profile part, so now you can prioritize jobs, gains, and pains according to their importance - from the most severe to least significant.
Lay out pain relievers
Pain relievers outline how the products and services can alleviate the pains you already described on the other side of the value proposition canvas. Different pain relievers address different pain points. Examples of pain relievers are reviews and videos to assure the quality of the product or a guide for a device.
To list the pain relievers, you can answer the following questions, if the product can…
- … produce cost savings, reduce the time and effort needed to complete the job?
- … make the customers feel better?
- … solve difficulties and challenges faced by your customers?
- … eliminate financial, social, and technical risks your customers encounter?
- … put an end to the mistakes customers make?
Outline gain creators
Gain creators are the ways in which you can improve your customers’ life and create benefits like positive emotions, cost savings, functional utility, and social gains. You need to assess how your product or service would help your customers receive desired or unexpected benefits.
The key questions are whether your products and services could…
- … deliver cost savings, save time and effort?
- … exceed the customers’ expectations in terms of outcomes?
- … make your customers’ life more manageable?
- … create positive social impact?
- … fulfill the customers’ dreams by helping them realize aspirations?
- … help make adoption easier?
After completing the listed steps, you need to measure the fit between the customer’s needs and value proposition. The target goal is for your gain creators and pain relievers to cover at least 50-70% of the customer gains and pains.
Examples of value proposition canvas
Let us consider five examples showing how you can work with value proposition canvas in practice.
Adidas x Parley
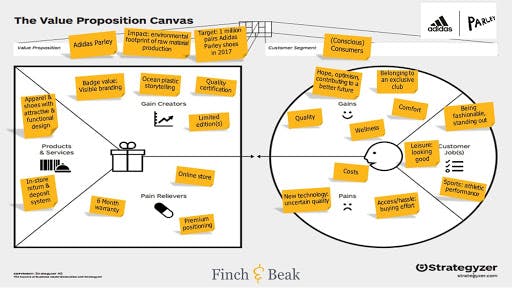
Source: finchandbeak.com
In 2015, the largest sportswear brand Adidas and ecological organization Parley partnered to produce a clothing and footwear collection. The brands developed the concept of sneakers made with recycled ocean plastic. Above is an example of the value proposition canvas for the Adidas Parley sneakers.
The main aspects of the value proposition canvas are the following:
- The product is sneakers for leisure and sports. The footwear design is functional and attractive, so it satisfies the consumers’ requirements;
- Visible branding and limited edition create the feeling of belonging to the exclusive club.
- Ocean plastic storytelling increases brand recognition in the world.
- 6-month warranty serves as a pain reliever so that consumers would have fewer doubts about the product quality.
Tesla
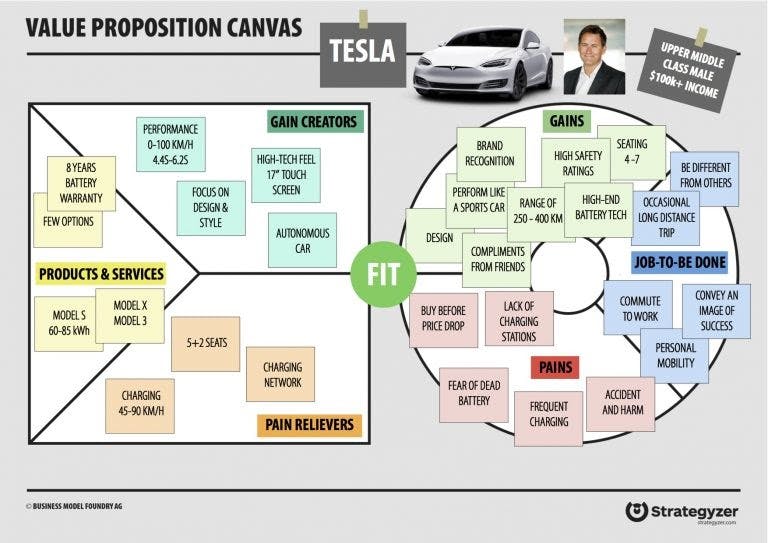
Source: designabetterbusiness.com
Value proposition canvas by Tesla shows an admirable product-market fit and a deep understanding of the target audience. In contrast to the other cars in the market, Tesla has a 17-inch touchscreen display and a beautiful design that makes it exclusive. The eight years battery warranty is a huge pain reliever. Besides the functional gains, the offering also provides emotional and social gains, including compliments from your friends.
Apple Pay
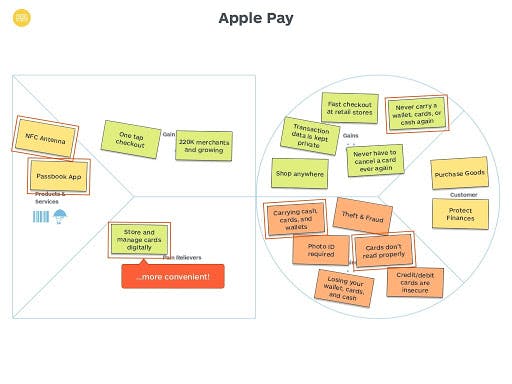
Source: slideshare.net
Value proposition canvas by Apple Pay provides the customers such gains as privacy, fast checkout at retail stores, and the ability to shop anywhere. The customers can store and manage cards digitally instead of carrying the wallet, cash, or cards. The offering’s features fully compensate for the main pain points: theft and fraud, lack of security, the necessity to have a photo ID, and the customers’ needs in finance protection. That’s an example of an excellent product-market fit.
Harvard University website
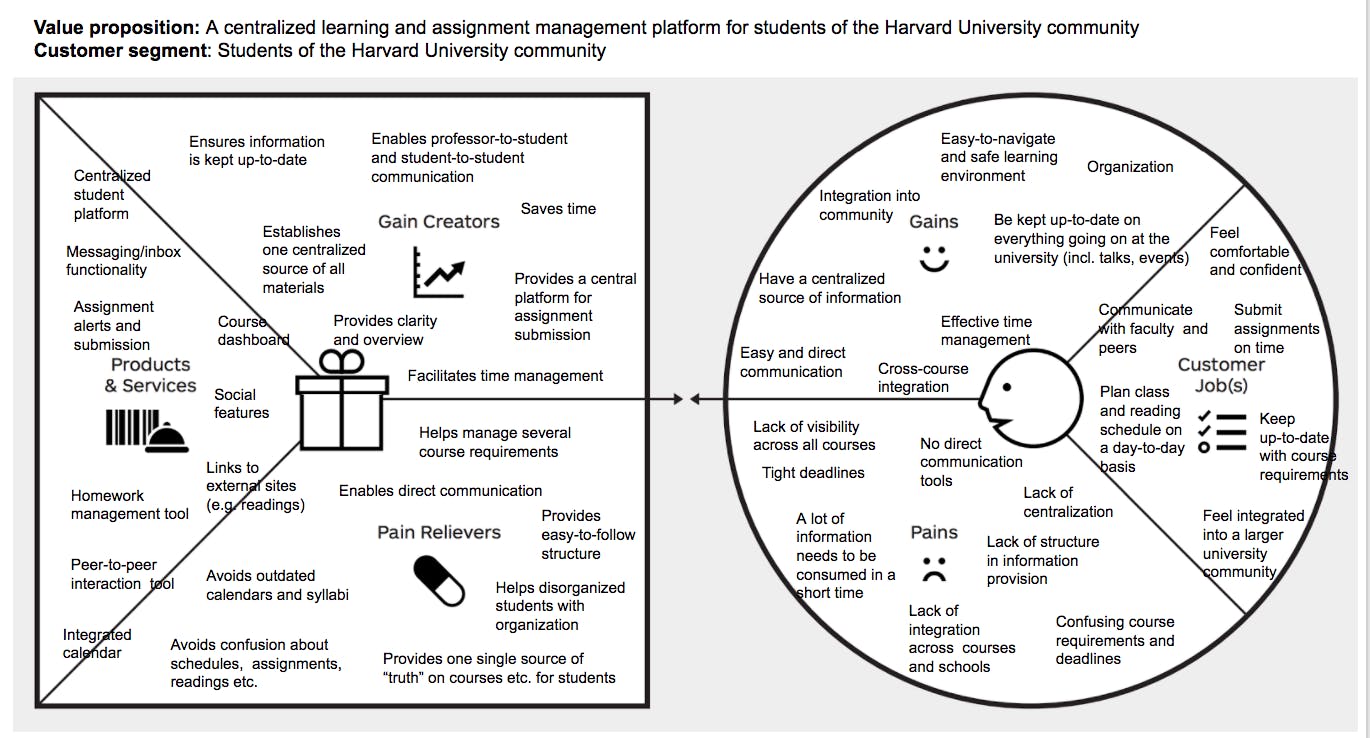
Source: medium.com
The value proposition canvas of the Harvard University platform demonstrates that the offering is aimed to improve multiple customers’ jobs. The platform helps relieve pains related to social (communication with faculty and peers, feel integrated into the community), functional (planning schedule, submitting assignments on time), and emotional (feeling comfortable and confident) jobs.
The website has many useful features that comply with such pain points as lack of centralization, absence of direct communication tools, and lack of visibility across all courses. The product serves as a peer-to-peer interaction tool, course dashboard, centralized student platform, and homework management tool.
Airbnb
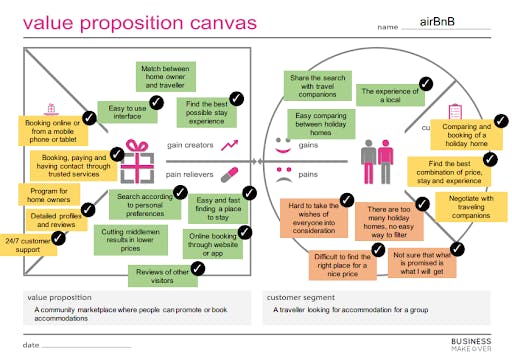
Source: businessmakeover.eu
The value proposition by Airbnb is targeted at the customer segment that comprises the travelers looking for a place of accommodation for the group. Their critical pain points include finding appropriate housing for a reasonable price, the risk of fraud, and a large number of holiday homes which creates difficulties with making a final decision.
Airbnb provides the opportunity to read the other visitors’ reviews and book the apartment online, which eliminates the risk of fraud. The customers can also search for housing according to personal preferences and easily find a place to stay. Thus, there is a good correlation between the product value and the customers’ needs.
When you need value proposition canvas
Value proposition canvas would help in a variety of business situations, such as entering refining your marketing strategy or finding new opportunities to market your product.
Finding the product-market fit
One of the most common situations where the value proposition canvas will come in handy is when you will be testing the product-market fit. Value proposition canvas will help you understand the needs of the target audience and create a product that will fulfill the requirements.
Entering a new market or customer segment
If you are going to sell into a new market or market segment, a value proposition canvas will help you to understand whether the market truly needs the product or service or not. The analysis of the customer problems will allow you to make the right decision.
Refining marketing strategy
Value proposition canvas is an easy way that will help your team visualize and improve the marketing strategy. It is also a relevant tool to create a winning go-to-market strategy for startups.
All-in-all, value proposition canvas is a systematic approach to defining a unique value proposition. It is a major step in driving overall marketing strategy because it covers the most vital aspects of your business — your customers and your product. Value proposition canvas encourages you to ask questions and perceive the world through your customers’ eyes, which is the keystone of success for any business.
