MECE framework: general principles and examples in marketing
Aug 24th, 2021

Structuring information comprehensively is essential in simple day-to-day activities. If you prepare a dish but forget to add salt, the dish already will not taste that good. The same goes for any challenge you take on. Logical structure helps clarify your ideas, improves understanding, and brings all the points together to reach the desired outcome. Structuring information contributes to better planning and implementation of the strategy.
The MECE framework is a powerful method for structuring ideas and information by breaking them into parts and organizing them according to the logical rules. The multi-use technique can be applied in various areas of marketing, such as market research, creating communication planning and advertising, writing, and content creation. We will describe the MECE principle and its common uses in marketing in greater detail below.

What is MECE framework?
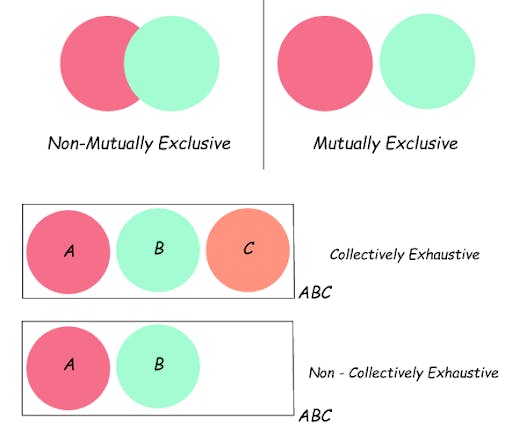
MECE framework is a way of sorting data into two groups that are mutually exclusive (ME) and collectively exhaustive (CE). The purpose of the framework is to help companies solve problems by breaking them down into basic components. According to the MECE principle, the information, including the issues, solutions, and ideas, can be structured into blocks without duplications.
The MECE framework is frequently used in consulting for creating the business strategy through the analysis of the possible options by the team members involved with the project. McKinsey applies the MECE principle to organize the data from customers’ businesses. Barbara Minto from McKinsey & Company created it in the late 1960s based on the ideas of Aristotle. Later the problem-solving framework formed the foundation of her Minto Pyramid Principle, the communication tool that implies grouping the key concepts into pyramids.
For example, you can apply the framework to the classification of the population according to age. If you categorize people according to two groups — above 60 and below 60, the division would be based on the MECE framework. On the other hand, a group of people aged 50-70 and another group under 60 would not fall under the MECE principle. People aged 50-60 would belong to both categories (not mutually exclusive), while people older than 70 would not fit into any group (not collectively exhaustive).
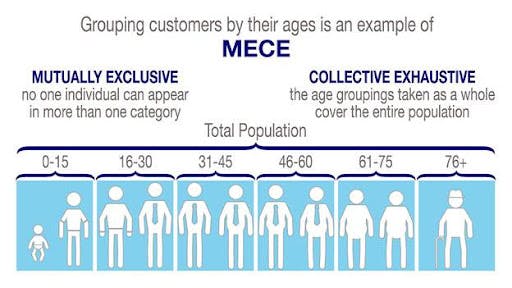
Mutually exclusive
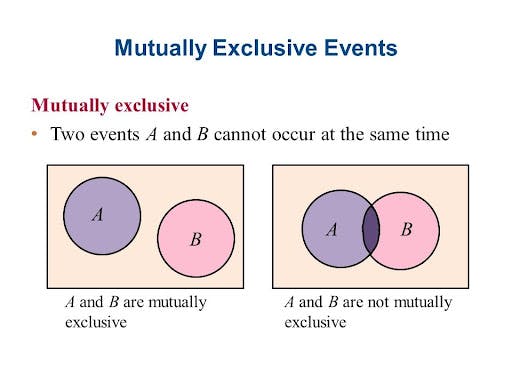
A mutually exclusive concept implies recognizing the pieces of data that are not related and do not overlap. It means that the components are entirely independent of each other and can not belong to the same two categories at once.
A simple example of the mutually exclusive principle is the probability theory concept that states that two events can not happen at the same time. If you roll the six-sided dice, you will either receive the result with three or with six. You can not get these outcomes at the same time, so they are mutually exclusive.
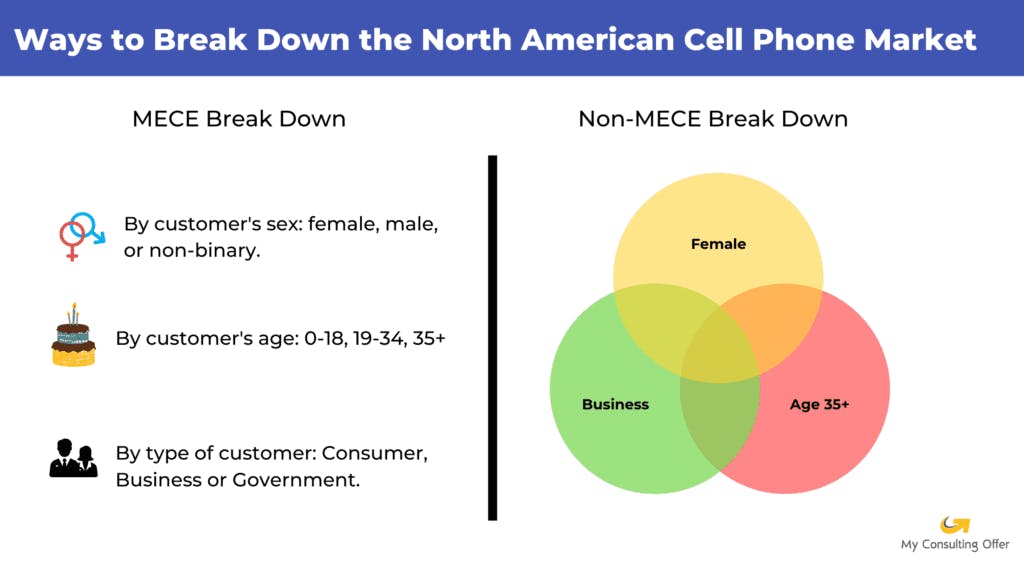
In the other example, we will consider the company that produces various types of food and decides what market category to choose next. If you assign each of your team members to meats, steaks, and proteins, this might lead to unnecessary work and a waste of time. In contrast, if you divide food into categories that do not overlap, such as grains, meats, and vegetables, you will make things much easier for your team. Each team member will be looking for a distinct set of information since the listed products cannot simultaneously belong to two categories.
Collectively exhaustive
This concept implies that when all data pieces are combined, they address the whole problem. In other words, a collectively exhaustive structure will group the related issues into buckets that cover the entire subject without missing details.
According to probability theory, the set of circumstances is collectively exhaustive if at least one of the events is going to happen. For example, if you roll the dice, events 1,2,3,4,5, and 6 are collectively exhaustive since they cover the complete spectrum of potential outcomes.
In the example with food categories, we reviewed meat, vegetables, and grains that are mutually exclusive. However, these categories do not include all types of food. If we add fruit, fish, poultry, and dairy, the groups will be both collectively exhaustive and mutually exclusive.
MECE applications in marketing
MECE segmentation is used for various kinds of essential business decisions, including customer targeting, product marketing, and operational activities. Now we will go over the use cases of the MECE framework in marketing.
MECE in market research
You can apply the MECE framework to determine the most valuable customers, identify the target market and segment it into groups with similar needs, buying patterns, and motivations.
Then you can prepare a survey following MECE principles. The framework helps you make sure that your questions are phrased correctly to avoid uncertainties and get reliable results for your study. The questions of the survey should be mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive. It means that the responses to the survey should contain all possible answers the respondent can choose. For example, suppose you are asking about the social media platforms used by the customers. In that case, the responses to the survey should include not only the existing platforms but also the answers “other” and “none of the above”.
With MECE, you can consider the demographic differences of your customers, such as age, ethnicity, gender, and geographic characteristics. If your goal is to conduct a thorough market analysis, you can group the essential topics into the following categories: industry and competition, consumer, product, go-to-market-strategy, supply chain, logistics, price, company capabilities, and others.
The MECE principle will also be helpful if your goal is to develop an international expansion strategy. In this case, when applying the MECE framework for market research, you can determine several vital categories: market, competitors, customers, company’s capabilities, and the product. Then you should evaluate the target markets in terms of size and growth rate, assess the company’s capabilities and costs required for marketing launch, and define your differentiation strategy.
MECE in creating a communication plan and advertising
MECE can be used in planning your advertising campaign when selecting the target audience. In this situation, the framework will help you reduce the overlap between consumers to a minimum while avoiding any shifts.
Let us categorize the customers according to age with MECE. We can exclude the little children up to 3-5 years old as they would never be your customers themselves. On the other hand, the children over 5 years old would start requesting such products as toys or sweets, so that they might become customers. As well, some products would only be relevant to older target audiences. Thus, we can identify the following groups of customers: kids, teenagers, young people, middle-aged people, and elderly.
For example, you are creating a marketing campaign for a dog food brand, and you aim to turn the people who sometimes buy the products from you and your competitors into loyal customers. Therefore, you need to target your advertisements at dog owners. At the same time, the ads targeted at brand switchers should differ from the promotions intended for non-loyal buyers.
According to MECE, you can create the buyer matrix with eight categories of consumers, including the following: heavy, medium, light, and non-category buyers, loyal customers, non-loyals, switchers, and non-brand buyers. Thus, the MECE principle allows you to segment the customers into distinct groups and understand which categories saw the advertising and how to analyze the sales outcomes.
Clear categories provide more precise and informative measurements after the advertising campaigns. The more accurate segmentation, the more confidence you will have about the results.
MECE in writing and content creation
MECE framework will be handy for creating blog posts and article outlines. The articles are often based either on a core problem or the author’s point of view. So first, you need to identify the main components of the topic and think about what information you need to cover the subject of the article comprehensively.
The next step is to identify the structure of the topic you want to present in the article. The articles on content marketing are often aimed at helping readers achieve a goal, such as increasing brand awareness or customer loyalty. Thus, the most suitable structure for the article will include separate logical sections, each dedicated to a particular aspect of the overall topic. The article will consist of the introduction, discussion, and conclusion.
Suppose you write an article on the topic “How to build a content marketing pipeline”. The logical structure will include three main steps: planning three months of content, producing articles consistently, and evaluating your publication. The paper will meet the requirements of the MECE framework, as there is no overlap between chapters, they provide a complete overview of the subject, and each section focuses on the separate stage of the process.
Conclusion
Understanding and routinely utilizing the MECE principle in day-to-day activities is crucial. MECE is a valuable tool for structuring plans, articles, and thoughts. It helps make sure that the problem is addressed thoroughly without uncertainties, unnecessary repetitions, or redundancy. Moreover, MECE guarantees that you will obtain a complete understanding of the issue, consider its elements and come to a logical conclusion. Thus, if you apply the MECE framework regularly, you will find other applications and use cases in many areas of your life.
