Complete guide to SaaS sales: models, metrics and best practices
Jul 1st, 2021

Contents
What is SaaS sales?
SaaS sales process
SaaS sales cycle
SaaS sales models
SaaS sales metrics
Best practices of SaaS sales
The primary goal of any business is to increase revenue. The means to achieve this goal is the sales process. It lies in several steps performed by the sales team to close more deals. The right sales process is as vital for the company as much as are the high-quality products. According to the survey company Gartner, 89% of companies believe that it is the customer experience that provides a competitive advantage to businesses.
Netflix is a shining example of a company that managed to implement an outstanding sales process. The company began by offering DVD mail-order services and then moved to stream videos. Now Netflix has over 193 million paid subscriptions worldwide.
Netflix’s sales process looks as follows: the landing page invites potential leads to join a free 30-day trial. Once the customer clicks on the call-to-action button, he sees the page with the package information. At this stage, Netflix is building the users’ trust. When the new customer clicks the “See the plans” button, they move to the third stage of the sales process — the plan pricing page. The fourth and fifth steps are the introduction page for creating the account and the sign-up page. Then the customer chooses a payment method after the free trial. At the final stage, the service collects payment information. This sales process performs well because it is straightforward and easy to use, the short steps move the visitors forward to take action, every page is sensitive to customer risk.
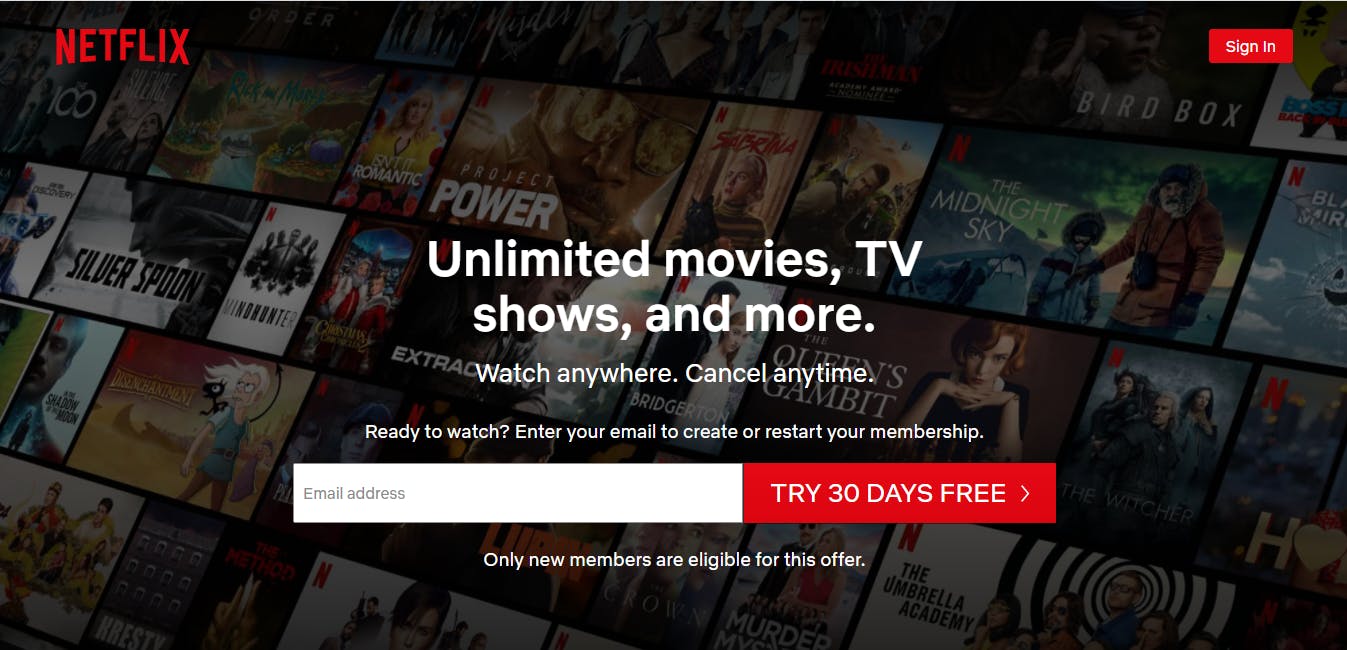
This is one of the many examples of the sales processes used by online businesses, many of which are so-called SaaS businesses. We’ll review the details behind such a process later in the article. But first, let’s go over the basics.
What is SaaS sales?
Software as a Service, or SaaS, is a software distribution model in which the software is based on subscription and provided by a vendor that hosts and maintains applications. In the software as a service model, the customer gets access to the application via the Internet instead of purchasing its physical copy and installing it on the local server.
As we have indicated above, the customer journey is of equal importance as the product itself. Thus, before the SaaS product launch, it is necessary to know about the stages of the SaaS sales process in detail.
SaaS sales is a complex step-by-step procedure of selling cloud-based software that customers access through a website or online portal to address business issues. The license period of the software is regulated by the contract. SaaS sales’ final goal is to make customers more successful by saving their time, money or helping them create additional revenue.
The SaaS sales process aims to acquire new customers and retain and grow existing ones. The customers buy monthly, quarterly and annual subscriptions, which create consistent income for the SaaS company. At the same time, the SaaS business model requires high initial investments from business owners. The average customer usually spends thousands of dollars on the software subscription over several years, so upselling is one of the most common techniques in SaaS sales.
SaaS is one of the most popular models for businesses in the cloud market due to the software’s easy accessibility — the customer needs only a browser and a stable Internet connection. The SaaS industry has been continually growing in recent years. According to the report published by BetterCloud in 2017, 73% of IT specialists said that 80% of their business applications would shift to SaaS products by 2021. 36% of the companies in 2017 were running almost entirely on SaaS. In 2020, the global SaaS market was estimated to be at 101.5 billion dollars. The most popular and innovative SaaS applications include Salesforce.com, Microsoft Office 365, Google Apps, Amazon Web Services, Zendesk, DocuSign, Slack, and Dropbox.
The SaaS applications are hosted by a service provider at a data center, so the customers save the costs for maintaining the hardware required for traditional software. The SaaS sales include a time-dependent aspect. In simple words, the company sells the monthly subscription instead of a more classical one-time sale. Thus, SaaS sales require a deeper understanding of the customers’ needs to meet their expectations.
SaaS sales process
The buyers of SaaS solutions often have doubts about purchasing the software since the price of SaaS solutions might be relatively high. To convince them to decide, you need to understand what stage of the customer’s journey they are at. The sales process should be based on determining the customer’s needs. Let’s review the steps of the process below.
Define the customer persona. The first step in the SaaS sales process is to create the ideal buyer persona. You need to define the benefits of your product and the customers’ pain points. The main characteristics to consider include age, location, income, personality traits, goals, and frustrations. To understand your audience’s requirements, you can conduct customer surveys and interviews, carry out market and competitor research, or analyze your website metrics like page views and visits to understand what information attracts your audience.
Create the sales pipeline. The sales pipeline is the visualization of every stage of the sales process. With the sales pipeline, you will be able to track how the users go through the stages of the purchasing process from lead to customer. It helps understand which activities bring higher income and how to encourage the customers to move to the next stage. You can also learn how well the sales process is working.
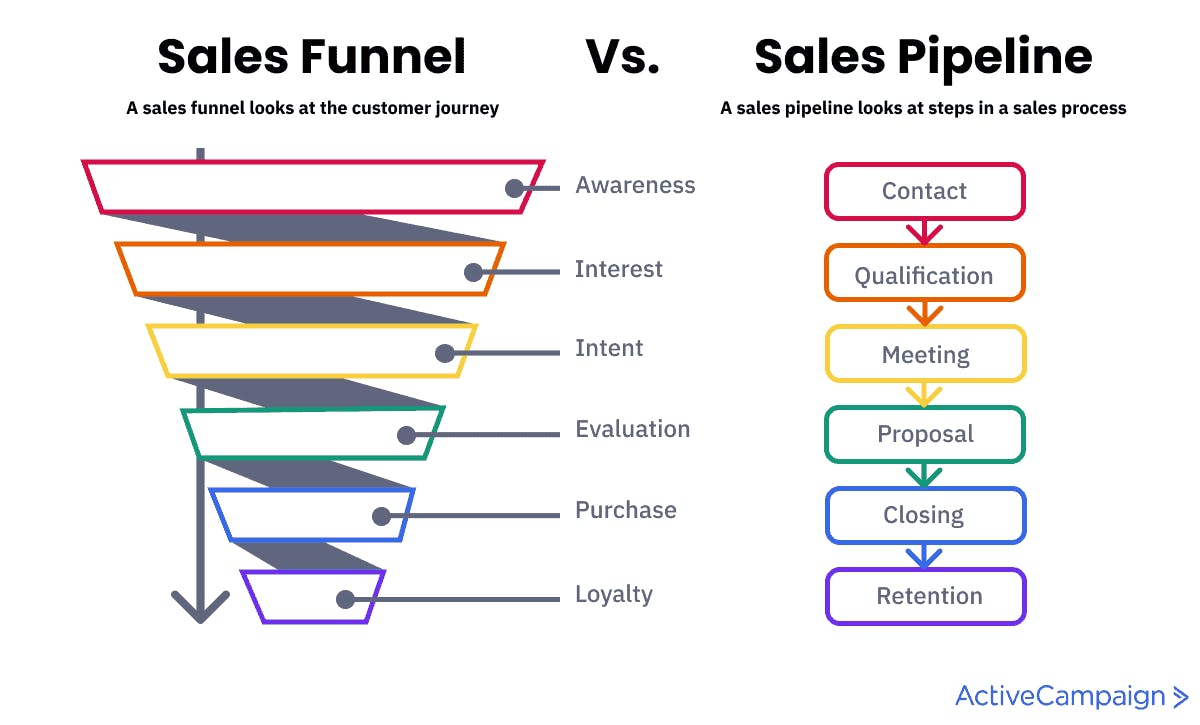
The sales pipeline can be broken down into six stages: prospecting, qualifying, presenting, handling objections, closing, and nurturing.
- Prospecting. The first step is to find prospective customers who are interested in your product. The most effective methods of attracting clients include social media, blog posts, online ads, newsletters, trade shows, and conferences.
- Qualifying. At this stage, you need to sort the hot leads from the cold leads by conducting research or guiding them through the landing pages of your website to confirm their interest. This step is critical because you have to understand whether your potential customers genuinely need your product or you should convince somebody else.
- Presenting. The next step is to contact prospective customers via phone, online and offline meetings, social media, or email.
- Handling objections. The most common objections in SaaS sales are: “The cost is too high” and “The software does not have the necessary features”. Make a list of possible objections and craft convincing responses for each.
- Closing. This step turns your prospect into a customer. Try to avoid offering discounts at this stage; instead, focus on presenting the value of your product in the best possible ways.
- Nurturing. The post-sale stage requires excellent customer support. Offer free guides, video tutorials, and other educational materials. Ask for feedback and reviews.
For SaaS companies, it is better to have multiple pipelines — sales pipeline and onboarding pipeline. This is a way to make sure that nothing is missed. The onboarding pipeline often consists of the following stages: user training, adoption, and configuration.
Ensure your team knows the product inside and out. You need to be prepared for technical questions from your customers. Spend some time using the software to be aware of new features. Learn about its pros and cons. The customer may describe the particular problem, so you should be ready to provide the solutions. You can offer short 15-minutes demos to show how your products will satisfy the customers’ needs.
Strive to improve the workflow. Try to boost customer experience using various communication channels, changing the content strategy, and collecting feedback. Customer reviews are a powerful tool to change your business for the better.
SaaS sales cycle
Understanding the SaaS sales cycle length is essential for business owners when forecasting the possible revenue. Several factors define how much time the product sales would take.
The sales cycle length depends on the product cost, product complexity, the number of decision-makers participating in the selling, the need for post-purchase setup and customization, etc. The higher is the price of the product, the longer the selling process would take. The sales cycle of the expensive products includes more detailed budget planning and a series of meetings to demonstrate the value to potential customers.
The second factor that influences the length of the sales cycle is the number of decision-makers. If the company is small, there will be fewer decision-makers involved, so the sales cycle will be shorter. The complexity of the product and availability of the free trials can also increase or decrease the sales cycle length.
SaaS sales models
The right choice of the SaaS sales model is crucial to the success of the overall sales process. There are three main types of SaaS models: self-serve, transactional, and enterprise. Cheaper products require a self-serve model, more expensive ones — the transactional sales model. The enterprise sales model will be the perfect solution for the most expensive products for giant customers.
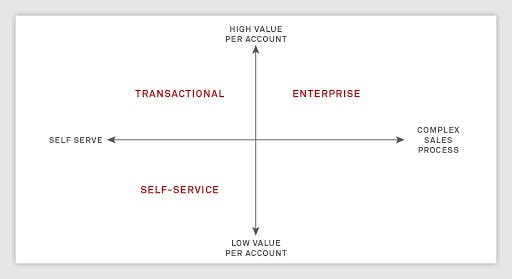
To choose the suitable model, you need to determine what stage your company is at in SaaS development and adoption. The chosen SaaS model will influence the size of your sales team, how you interact with customers, and who are your potential buyers.
The self-serve model
This model is aimed at small and micro-businesses because the cost of hiring a dedicated sales team is often too high for this kind of company. The self-serve model does not imply sales. The customers manage the process themselves — they buy the product by themselves and use the solution without consulting a sales representative.
The benefit of the self-serve model is low investments along with significant revenue. Marketing plays a crucial role in this model because it drives the purchase process by publishing content, creating awareness, and automating most interactions. The company has to make sure that potential customers have the necessary educational materials to tackle issues on their own.
The transactional model
The transactional model was designed for middle-sized customers. It is a hybrid of self-service and enterprise models. The transactional sales model requires the participation of the inside sales teams resulting in the higher price of the product. Together with real-time assistance from the inside sales team, it creates an automated lead generation strategy. Both of these elements work in combination to convert leads into customers.
The transactional model provides a list of advantages for businesses, such as premium SLAs, signed long-term contracts, and the ability to solve the problems through experts’ participation. Despite the high risks, the transactional model is very profitable, bringing a high volume of sales. The customers receive not only the educational content and self-serve tools but also the opportunity to consult sales representatives if the problem arises. Additionally, this last aspect creates a feedback loop for the company itself, making it easier to find new growth opportunities based on first-hand customer requests.
The enterprise model
The enterprise sales model is the most complex one. It is suitable for the most expensive solutions and large companies. Enterprises often need a significant amount of time to make a purchasing decision, so the selling company should involve both in-house and field sales representatives in the process. The high-end marketing in this model contributes to brand awareness, relationship-building, and trust.
The other characteristics of the enterprise model include perfect customer service in the form of technical support and onsite issue resolution. The enterprise model would often require the ability to customize or white-label your solution according to the client’s needs. It should be noted that the enterprise model has a very high degree of risk. Also, it is quite expensive due to the considerable number of people involved in the process. But it allows businesses to attract larger clients, retain clients longer, and expand the services within the cooperation with each client, so the added value outweighs the costs in the majority of cases.
SaaS sales metrics
The SaaS sales metrics are important indicators of the company’s health. The single sale is just the beginning of the customer’s journey. However, the sales team should not only generate new sales but also attract new prospects, turn them into customers, and upsell to the existing customer base. With the sales metrics, you can effectively track whether the implementation of your sales process has produced positive results. There are ten main metrics worth paying attention to.
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR). This is the income your company receives every 30 days. It depends on the value of your customers’ subscriptions. To calculate the monthly recurring revenue, add up the customers’ fees over the period of the last 30 days.
- Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR). Annual recurring revenue is a metric that shows how much income the company earns on an annual basis. Annual recurring revenue comprises monthly recurring revenue multiplied by 12.
- The number of sales qualified leads (SQL). A sales-qualified lead is a potential client who is ready to become a customer in comparison with other leads. SQL does not necessarily intend to purchase the product but judging from their actions, you can say that they are ready for the next stage of the sales process.
- Lead velocity rate. This metric displays the growth of qualified leads from month to month. To measure the lead velocity rate, use the following formula: Leads This Period - Leads Previous Period) / Leads Previous Period.
- Demo-to-trial ratio. With the help of this metric, you can track how many of your demos turn into trials and then become closed-won deals. The poor results mean that you need to change something in your demo process or qualify your leads better to avoid demos to prospects who are not yet ready to purchase.
- Closed won/lost. Closed-won deals are the deals when the customer signs the contract or provides payment. In another case, the deal is “closed-lost”. The ratio of closed-won deals to closed-lost ones tells about the efficiency of the sales representative’s work. It is also the way to build better revenue forecasts based on your marketing and sales activities.
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC). This metric shows the cost of signing the new customers. Among the factors that influence customer acquisition cost are the marketing team’s efforts and advertising budget, your pipeline conversion rate from leads through prospects to customers, and a number of other aspects, which influence customer acquisition in the particular business. The calculation of customer acquisition cost is simple: divide the cost of marketing and sales expenses by the number of users gained in the same period.
- Customer lifetime value (LTV). Customer lifetime value is the amount of overall revenue generated by the client during the interaction with the company. When customer lifetime value is higher than the customer acquisition cost, your business is succeeding, and you can work on growing the volume of new customers you acquire. Once the CAC starts to grow larger than LTV, it’s time to look for ways to decrease the acquisition cost or increase the lifetime value. This can be done by creating incentives for customers to stay longer with you and finding ways for an average customer to spend more on your product.
- Churn rate. Churn rate is the percentage of customers you lose monthly or yearly. You can compare this rate with the industry benchmarks to determine the company’s financial strength. To calculate the churn rate, you need to divide the number of customers you lost by the total number of customers during the same period and multiply by 100. The lower your churn rate, the better it is for your business - effectively, it shows that your new customers stay with you longer, so you can rely on their revenue in the months and years to come.
- Net Promoter Score. With this rate, you can predict business growth and measure customer experience. You can calculate NPS using one main question: How likely would your customers recommend the company to their friends or colleagues? Depending on the answer between 1 and 10, the customers can be categorized as promoters (score 9-10), passives (score 7-8), and detractors (score 0-6). Promoters are loyal and enthusiastic customers and are the ones who’ll recommend your product to others. Passives are satisfied with the product but not loyal to the brand. Finally, detractors have had a negative experience with the company. Your goal is to grow the number of promoters while decreasing the percentage of detractors.
Best practices of SaaS sales
Besides selecting the sales models and analyzing metrics, every SaaS sales leader should apply some fundamental principles to boost performance in the team. The following tips are the principles used by professionals in the industry.
Upselling is fundamental to success. Upselling has an enormous impact on the growth of businesses. The leaders in the SaaS industry achieved success due to upselling. However, it might seem complicated for the sales representatives to re-engage with the clients because they already know all the flaws. You need to examine the user’s account and find a reason why the customer would agree to upgrade to the premium version of the software or grow the number of users in their account.
Take advantage of CRM tools. CRM tools and social media offer new opportunities for sales representatives to collect and organize data. Most CRM tools allow you to overview your sales activities and interactions with the customers and analyze the results.
Marketing has a direct influence on sales. Sales and marketing are two interrelated processes. The marketing department plays a vital role in establishing the relationship between the sales team and the potential customers. The marketing metrics help track visitors, closed deals, and conversion rates. The marketing team can help sales representatives recognize weak points and reduce costs of customer acquisition.
Creating a strong SaaS sales team does not happen overnight. It requires constant learning, analyzing the metrics, and improving the processes. Despite this fact, you have already made the first step towards your goal — you have read this article, and now you’re ready to start your SaaS sales journey.
