Pain points: how to identify and solve them?
Aug 31st, 2023

Contents
What are customer pain points?
Types of business pain points
How to identify customer pain points?
How to solve customer pain points?
It will be challenging to retain clients and provide them with outstanding products if you don’t know what problems they experience in their daily lives. Identifying customer pain points lies at the core of developing both your sales and marketing strategies.
Salespeople must understand customer pain points to tailor sales pitches to clients’ requirements and position a product. Marketers should identify these problems to promote the offering compellingly. Therefore, you can increase customer satisfaction and earn loyalty by identifying and addressing your customers' pain points.
There is no universal strategy for identifying client pain points. Moreover, it is often more complicated than it seems. In many cases, customers are not aware of the underlying causes of their problems. Once you learn about these challenges, you may help them make purchasing decisions. In this article, we will consider how to uncover customer pain points, describe different types of problems, and explain how to solve them.
What are customer pain points?
Customer pain points are consistent or recurring problems existing or potential company clients face when interacting with a product or service. These might range from a necessity for a particular product to dissatisfaction with the solutions already on the market.
The other definition of pain points refers to flaws in a product or service that may discourage customers from buying it. One of the most common customer complaints, for instance, is that they do not like waiting for products from abroad and want to test them before making a purchase. As a result, to solve this pain point, you can launch an online store where you can pre-order items from several brands or provide two-day shipping with a flexible return policy.
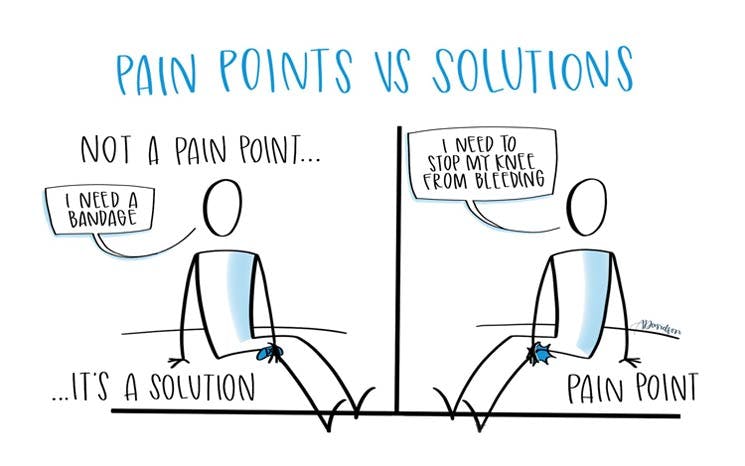
If you ever expressed dissatisfaction with too much time spent in a queue, poor customer service, or the need to go through a tedious registration process, then you know what a customer pain point is. In the following section of the article, we will explain the types of business pain points in greater detail.
Types of business pain points
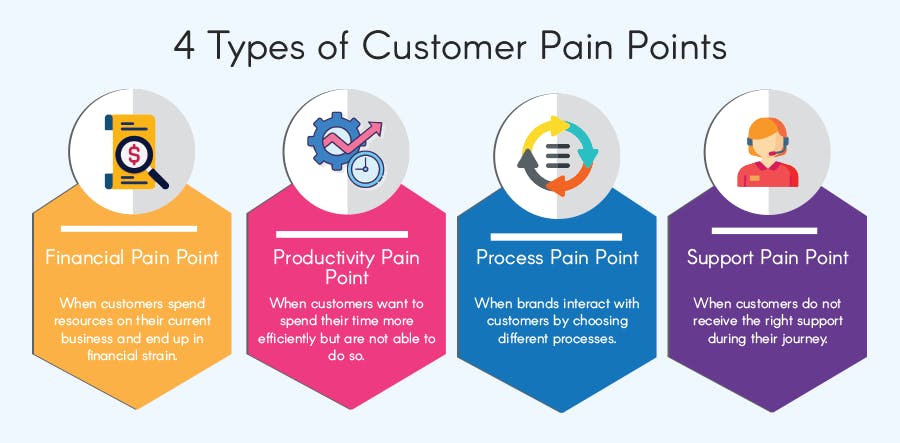
There are countless possible pain points that customers can face. We will group them into five categories to illustrate more general issues.
Financial pain points
As most people take into consideration price, value, and cost savings, financial pain points are one of the most crucial types to consider. Many companies believe that setting the lowest prices is the easiest way to increase sales. Even though some clients pay attention to picking the cheapest products, other factors also influence the sales process.
One of these factors is product value. Customers face this financial pain point when they believe they are not receiving enough value for their money. For example, a company’s product may be of lower quality than rival offerings, require costly maintenance, or must be replaced frequently. Other examples of financial pain points include expensive subscription plans, additional fees, and a lack of price transparency.
Productivity pain points
Productivity pain points are related to efficiency. Consumers experience these problems when they waste their time and do not get the desired results. For example, users may experience frustration if a product is too complex or if its usage requires completing too many steps.
The other productivity pain points are the time-consuming buying process, the inconvenience of using a product, and difficulty navigating your website or finding the information consumers need. Customers want an easy and intuitive experience when interacting with companies online.
Business productivity issues cost customers money. The final consequence is the same whether it's in the sales process or utilizing an app interface: inefficiencies and consumer frustration. Since companies quickly abandon products that negatively affect their profits, these problems should be immediately addressed.
Pain points in the buying process
Design shortcomings that lead to unnecessary steps, unclear instructions, or slow user experiences are the source of process pain points. It applies to any situation where consumers must take unneeded actions to achieve their goals. Examples of such cases may include the inability to reach the correct department, a lack of payment options, limited hours of operation, or the absence of timely updates.
Pain points in the buying process can result in lost sales. Although many customers can ignore these issues, they are less likely to make a repeat purchase. Moreover, prospects may assume that working with your organization would be challenging if your sales process is lengthy and complex.
Logistical pain points
Most consumers want to know when they can receive their order after completing the checkout procedure remotely. Customers want to be informed about the status of their order, any delays or issues, and how to contact customer service if necessary.
Unclear or nonexistent tracking options are logistical pain points. To tackle these problems, practicing transparency, improving infrastructure, and offering logical tracking alternatives are crucial. It's also critical to employ reliable delivery methods to minimize missing or damaged orders.
Support pain points
Common customer pain points are related to support. When customers have an issue, they want it resolved quickly and efficiently. The problems typically involve difficulties with access to sales representatives, slow response times from customer service, unhelpful support agents, or an inability to self-service. Furthermore, when a company operates both physical and online stores, problems can arise due to a lack of communication between departments.
The faster these support trouble areas are fixed, the better for your business's reputation in terms of customer service. By improving communication channels and providing regular updates, you can alleviate support pain points and improve the overall customer experience. In addition, if you offer prompt and user-friendly customer service, you can increase client satisfaction and loyalty.
Customer pain points play a vital role for your company since they reflect various crucial business processes and demonstrate how successfully your organization handles its problems.
How to identify customer pain points?
Further, we will provide recommendations to help you identify client pain points. Let us discuss these methods in more depth.
Conduct customer research
Though we grouped pain points into categories, they are unique to each person. To learn more about the issues people face, conduct primary market research through surveys, interviews, and focus groups. Ask open-ended questions and encourage people to express their opinions in their own words. Use sales techniques like SPIN selling to direct the conversation and help you learn about the customer's problems and how to solve them.
You can also add live chat to your website so visitors can ask questions and report problems. Your sales team will get a ton of customer-driven data and determine issues that frequently annoy clients. By using live chat, you will be able to save and categorize information for further analysis.
Talk to your sales representatives
Your customer success and sales teams receive direct customer feedback on the problems they encounter and the changes consumers want to see. When you speak with your staff, pay attention to the issues that come up most often. These pain points might be the ones that have the most impact on your revenue.
You can spot underlying trends and even pain points that some customers are not aware of since the sales staff will have a unique viewpoint on the problems that clients face. Ask your sales representatives about the main factors that deter promising marketing qualified leads, the features that often lead to a sale, and the characteristics your product lacks.
Remember that client pain points change over time. Encourage your staff to keep sharing customer feedback after the initial interview so that you can monitor changes in consumers’ experiences.

Use social listening
Monitor online reviews and analyze customer feedback on social media to understand what people think about your products. To find client opinions, you can check review sites for businesses, comments on online marketplaces, and the product page. You can also examine your customer service tickets to discover your clients' problems.
Even though reading bad reviews is never enjoyable, they can help you understand people's problems and find areas for improvement. Getting the most out of the information on social media should already be a vital component of your marketing strategy.
The ability to often learn additional details about reviewers is another advantage of conducting market research online. For instance, you can find their personal information and understand their purchasing patterns and perceptions of your rivals.
Perform competitor analysis
You can use competitor analysis to understand how your rivals promote their products and services to the same target market. They could identify client pain points you hadn't considered and market their offerings more effectively. It is also a great way to assess what customers do not like about products.
For example, if your competitors offer products with long-lasting guarantees, customers may be concerned about the product breaking, which is a pain point. Thus, examining the offerings your rivals provide and how they resolve customer problems may give you valuable insights into the challenges that your target market faces.
Put yourself in the customer’s shoes
Besides data and analytics, paying attention to the emotional aspect is critical. Look at your company and product from the customers’ perspective. Consider how your consumers perceive their value throughout the customer journey. Think about whether they receive personalized help. Analyze whether they speak with the same customer support reps when they contact your company to ensure consistency and familiarity. Check whether your sales agents can immediately access customers’ prior transactions and interactions.
To understand customers’ pain points, you can also use a framework called Jobs-to-be-Done. According to this approach, developed by Clayton Christensen, customers purchase a product or service not to satisfy a basic need. Instead, they hire a product to do a specific job, such as making them feel more organized.
In other words, your clients may not consider your offering the same way you do. They think about how your product or service can benefit them. Therefore, you should analyze what job your product does for the consumer. Once you understand this, you can start asking the right questions that encourage your clients to share their problems with you.
You have learned to identify customer pain points, so let us discuss how to solve them.
How to solve customer pain points?
Now you know about common customer problems and challenges. We will look at some solutions you can provide to solve customer pain points and improve your brand's reputation and customer loyalty.
Step 1. Analyze and interpret the feedback
As you learn more about the problems that your clients are experiencing, you can organize, analyze, and interpret the feedback. Graphs, tables, reports, and software are some methods and tools you can use to simplify the process. Your goal is to find trends, gaps, and patterns to help you understand how to address customer issues.
Keep in mind that satisfied customers tend to leave comments less frequently, so feedback can be unbalanced, with replies generally being more negative. Therefore, do not use feedback as an indicator of overall quality. Instead, gather data on the areas that, according to customers’ opinions, need to be improved.
Step 2. Prioritize and document the issues
First, you can group the issues into categories, prioritize the most urgent and crucial problems, and then develop a plan to deal with them. Categorize the pain points according to the type, priority, and number of complaints.
Finding a solution will probably require various resources and the involvement of different teams, so you need to classify the issues according to the types we mentioned above. Consider whether the problem is related to productivity, finances, processes, logistics, or support, and then assign staff members responsible for implementation.
You can categorize the problems according to priority using the following scheme:
Group 1: Although the client is dissatisfied, they can still use the product.
Group 2: The client is disappointed but will continue using the product.
Group 3: The consumer is obviously dissatisfied and can choose another product.
Group 4: The customer is actively looking for a different product to substitute yours.
Group 5: The client has given up on finding a solution.
Finally, group the issues according to the number of complaints. Sometimes, the matter affects only one person, so it makes more sense to address it individually rather than devote months to creating an entirely new feature. However, an urgent pain point that many people have raised may frustrate potential customers and has to be addressed sooner.

Step 3. Examine your internal procedures
Internal business procedures may directly affect client pain points, especially if your company offers a service. You may free up resources and use them to satisfy client demands by resolving inefficiencies in your company's processes.
Hold a few meetings or brainstorming sessions to come up with solutions, and take into account which employees might contribute to the discussion about particular pain points. Most likely, your staff will need to conduct further research to learn how other businesses handle similar challenges or to get additional information on customer interactions with a product.
At this stage, you must prepare a list of tasks, assign duties, and set deadlines. You can start with small pain points that you can resolve at once. These minor problems frequently have a significant impact on consumers' purchasing decisions.
Step 4. Create a library of useful content
By providing content that people can read when they're seeking information on a subject or a solution to their problems, you may alleviate any pain points your clients may be experiencing. You can launch a blog, create a knowledge base, provide explainer videos, or dedicate a website section to educational content about your product.
Then, use Google Analytics to find the most popular posts and the ones that readers prefer to spend the most time on. It provides you with even more knowledge about your clients so you can create more relevant and personalized content to make them feel valued.
Step 5. Demonstrate empathy in your responses
You need to put empathy first in your customer service solutions. Customers will feel appreciated if you demonstrate an understanding of their problems from a human perspective. Personalized support is one of the key elements of customer service that leads to client retention.
Your customer service representatives should be user-friendly and reply with a fair amount of respect. After successful interactions, you should ponder assigning the same agent to a client to maintain a high degree of continuity.
Empathetic responses also depend on how much prior information is available to your representatives. Your agents will be able to respond to requests better if they can immediately access previous interactions.
Overall, understanding and addressing your customers' pain points is crucial for the success of your business. By putting yourself in your customers' shoes and providing solutions to their problems, you can build a loyal customer base and improve your bottom line.
