Essential guide to pricing strategy: how to, types and examples
Mar 17th, 2022

Pricing is one of the paramount challenges faced by companies. Prices should not only correspond to the existing market conditions but also cover the company’s expenses, take into account the competitors’ pricing and allow the organization to make a profit. A pricing strategy should also maintain balance while addressing customers’ needs and generating revenue.
Moreover, when it comes to pricing, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Instead, you need to continuously review the pricing strategy and adapt it to changing market conditions and competitive environment. Thankfully, a variety of pricing models and approaches will help you identify the best pricing that will help you find the sweet spot between your clients’ ability to pay and your financial goals. This article will describe the most common pricing strategies and provide examples of their successful implementation.
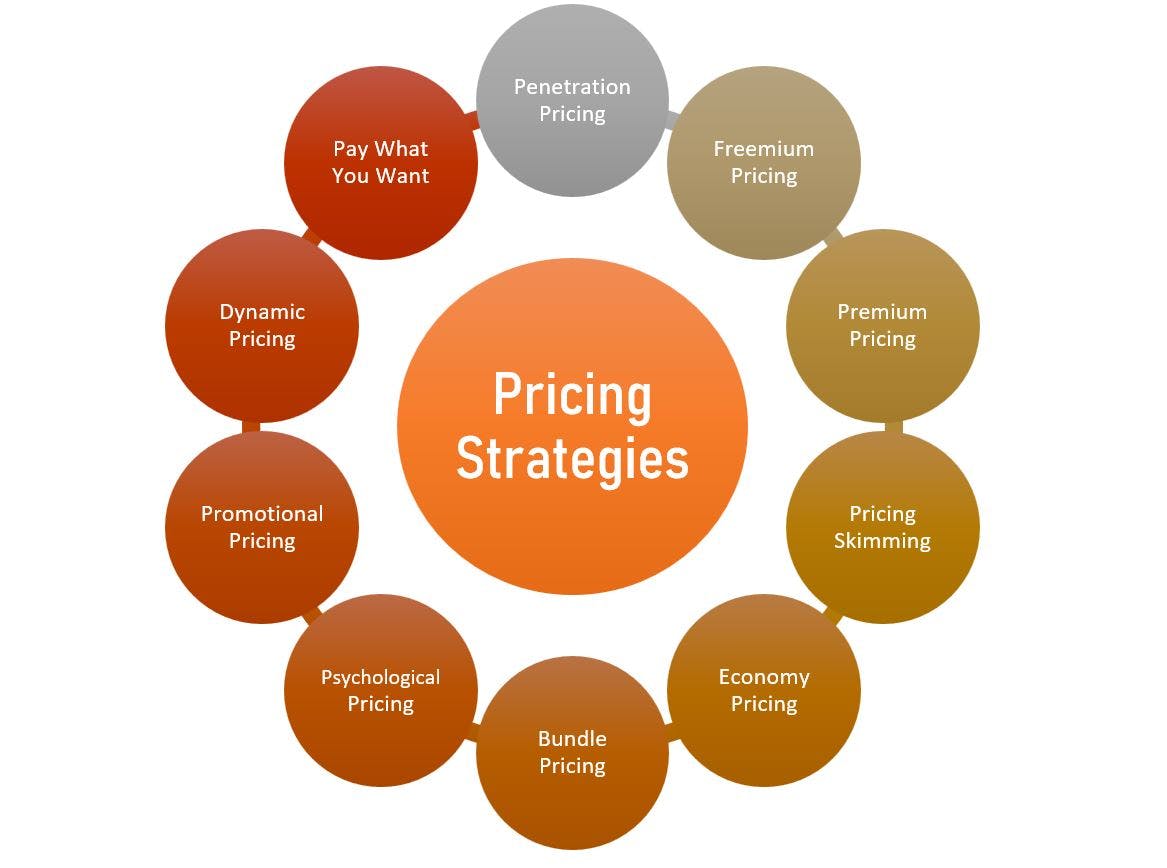
What is a pricing strategy?
Pricing strategy is a method of determining the most appropriate price for a product or service. This process takes into consideration market and consumer demand and focuses on maximizing profits and shareholder value. When developing a pricing strategy, businesses consider various factors, such as marketing goals, financial objectives, target customers, brand positioning, input costs, trade margins, and product characteristics. The external factors that affect pricing strategy include competitor pricing, economic and market trends.
When selling a product or service, a company may employ a range of pricing strategies. Before deciding on the most suitable pricing strategy, senior executives need to analyze the brand positioning with respect to its competitors and to the customers’ perspective, price segmentation or establishing different prices for the same products or services and competitive pricing response strategy or the way to respond to competitor price changes. It should also be noted that pricing strategy greatly depends on economic, cultural, and industrial conditions and varies from one organization to another.
Many articles on pricing use the terms pricing strategy and pricing model interchangeably. However, there are some notable differences. A pricing model deals with the implementation of a pricing strategy. Pricing models rely on quantitative data. Some of the most popular pricing models include hourly, project-based, retainer, and performance-based approaches. The retainer model, for example, is when a business owner charges a monthly fee for a specific amount of time spent on the task or deliverables.
Pricing strategy, in contrast, is how the seller utilizes pricing to accomplish defined business goals. The term refers to a consumer’s reaction to particular prices. In this guide, we will review pricing strategies and the steps needed to create one.
Types of pricing strategies
An effective pricing strategy allows you to strengthen your position in the market by gaining consumers’ trust and meeting your business objectives. The listed approaches will be based on various characteristics, such as product value, expenses you need to cover, the purchasing power of your target market, and competitors’ pricing. Let us compare different types of pricing strategies, their advantages and disadvantages.
Penetration pricing strategy
The main idea of the penetration pricing strategy is to encourage potential buyers to purchase the product by offering a lower price during the initial release. This pricing strategy helps new businesses enter the market and attract customers. Penetration pricing utilizes low prices to raise awareness about a new product among a large number of clients. After some time, the company raises prices to maximize profits and demonstrate the increasing value of the product.
According to penetration strategy, a brand initially lowers prices to gain market share and build a customer base with the goal of keeping new clients once the prices go back to normal. Due to this reason, penetration pricing is usually applied for a limited time, and it is not suitable as a long-term strategy. Moreover, there is a considerable risk that the buyers may prefer the brand at first but then choose the competitor as prices rise.
Landlocked Airlines employed a penetration pricing strategy to encourage customers to use its services during certain seasons. This approach proved to be effective for a small airline company. Landlocked Airlines promoted its services during the winter holidays. The company reduced prices for inter-state trips, which helped it earn a good reputation and attract many new customers who would book more expensive tickets in the future.
Competitive pricing strategy
A competitive pricing strategy is based on using competitors’ prices as a reference point to set your product prices. This strategy does not take into account consumer demand or product cost. The approach is suitable for an over-saturated market as slightly different prices can play a critical role for the customers while the characteristics of the products remain the same.
There are three options for businesses that follow a competitive pricing strategy. The companies may set prices below the competition, at the competitors' level, or above the competition.

If the company sets higher prices for the products than its competitors, it should justify the pricing by providing additional features or special payment terms. When the company is going to charge a price below the market, there is a chance of potential losses. The profits from the additional products can compensate for the expenses on the product priced below the market. If a business sets the same prices as its competitors for similar products, it may distinguish itself through outstanding product marketing.
Pepsi and Coca-Cola are perfect examples of competitive pricing strategy. This is because the brands are very similar in terms of the quality and characteristics of the products. However, Pepsi is usually slightly more expensive than Coca-Cola. So will typically have smaller total sales volumes with better profit margins, while Coke will usually achieve necessary overall profits through larger sales volumes.
Skimming (or high-low) pricing strategy
Skimming strategy is when a business sets the highest initial price for a new product and then cuts it once there is lower demand. The skimming pricing strategy is widely used in technology markets where companies aim to reimburse R&D costs. The tech companies producing devices like smartphones and video game consoles usually price their products according to this strategy as gadgets tend to lose relevance over time.
This approach targets early adopters or customers who have lower price sensitivity. It happens for several reasons: these people’s need for the product outweighs their desire to save money, they usually have higher income or better knowledge of the product’s value. Companies apply a skimming strategy for a limited period to recover their investments in product development. To obtain greater market share, businesses should use other approaches like penetration pricing strategy after some time. However, the skimming method may irritate consumers who purchased the product initially and attract competitors who notice the sudden decrease in prices.

Apple uses a skimming pricing strategy to gain the highest profit in a short time instead of getting the maximum sales. The company also applies this strategy to differentiate itself from the competitors in the market. Furthermore, Apple made minor adjustments in the skimming pricing strategy. The company charges high prices for the new products and then justifies them by increasing the value of the products in future versions.
Premium (or prestige) pricing strategy
Premium pricing strategy is also known as prestige pricing or luxury pricing. According to this strategy, companies artificially increase prices to create the perception that the products are exclusive, high-end, or luxurious. The strategy is based on consumers’ belief that expensive products have a solid reputation, are more trustworthy or attractive, and symbolize excellent quality and distinction. Premium pricing focuses more on the product’s perceived value than its actual value.
Customers of the brands sticking to the premium pricing strategy are typically not price-sensitive, so they are ready to pay more for the latest trends. Technology and fashion brands use this approach as they aim to provide value and status through their products. The drawback of the strategy is the difficulty of implementation. The success depends on the physical locations of the stores and target customers.
Starbucks is an example of a premium pricing strategy. The coffee company’s customers choose its lattes and signature coffee products over lower-priced competitors, such as Dunkin’ Donuts and smaller or local coffee chains.
Value-based pricing strategy
This strategy relies on determining the price of the product according to its value for the customer. A value-based pricing strategy is often used when the value of the product to the customer exceeds the cost of production. The businesses that use this strategy always target one specific customer segment or a single customer if it is a B2B company. The value-based approach is not applicable in the case of multiple segments as it would be difficult for marketers to determine the appropriate price for each one.
The strategy will not work well for the “blue ocean” products as this pricing method works if the product has a competitor’s alternative offer. First, the marketers have to use the competitor’s product as the criterion for establishing a value-based price. Then it is essential to determine the product’s unique features that distinguish it from the competing option. Finally, the marketers need to calculate the value of the differentiated features.
Supreme, an American streetwear brand, differentiates itself from competitors by emphasizing the exclusivity of clothing while maintaining prices relatively cheap and affordable. The brand always keeps a minimal inventory and never produces a large number of items. You cannot buy Supreme clothing in large retail stores, their supply is restricted. Owning limited items sold by Supreme makes its owner a much more fashion-conscious person. This strategy creates a sense of originality of the products while increasing their desirability. As a result, the brand has a unique value that you cannot get from owning any other piece.
Dynamic pricing strategy
Dynamic pricing strategy, sometimes also known as time-based pricing, surge pricing, and demand pricing, establishes prices based on various factors, such as competitor pricing, customer demand, market, and supply. When implementing a dynamic pricing strategy, the companies use data collected from customers or react to changing market conditions. Then businesses adjust the prices for comparable goods to correspond to consumers’ capacity to pay.
The companies that typically use dynamic pricing strategy are hotels, airline companies, and entertainment facilities. These organizations apply specific machine learning algorithms that analyze demand, competitor prices, and other factors to customize prices to current market conditions or customers’ willingness to pay. The dynamic method is also suitable for large businesses like eCommerce platforms and retail stores as implementing the strategy can be quite expensive.
Uber charges a price for a ride depending on the route, traffic, and rider-to-driver demand at the moment. The algorithm or service rules consider these factors when determining the prices.
Cost-plus (or economy) pricing strategy
A cost-plus strategy is one of the easiest methods to set up the price for the product. The strategy takes into account only the cost of producing the product. Then you need to add the set markup percentage to the costs and sell the product for the total. Thus, to derive the price of the product, you need to add material costs, labor costs, shipping costs, marketing, and overhead costs to a markup percentage.
Retailers who sell physical goods often use this method. The advantage of the cost-plus strategy is that it is easy to calculate. If all your production and labor costs are fixed, this pricing strategy can generate consistent profits. However, the method does not consider market factors, such as customer perceived value or competitors’ prices.
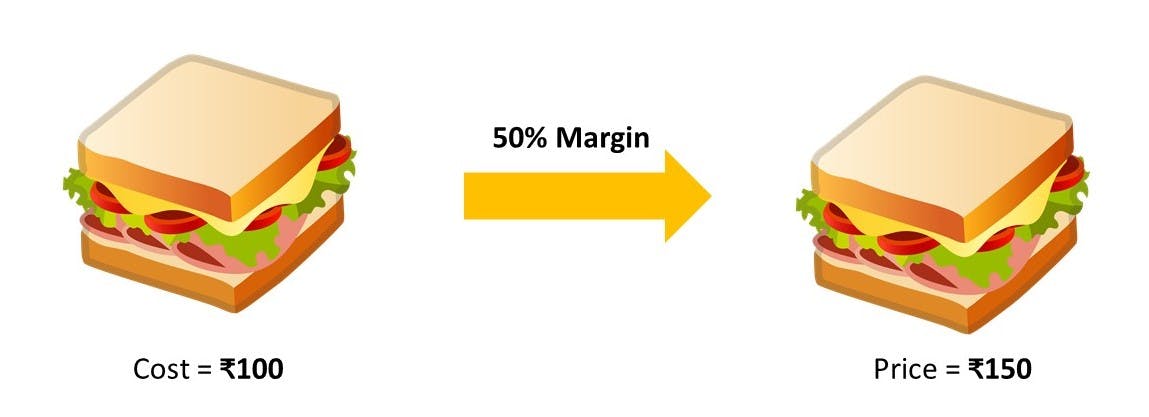
Let us imagine the company that produces jellies and jams. The production cost of a jar of wild blueberry jelly is $1.50 per 250 ml. The company is going to add a markup of 40%. Thus, the price of the jelly in the shop will be $2.10.
Target pricing strategy
Target pricing strategy is a method used by companies to establish the product price on the basis of market prices. A target price is an expected price the potential buyers are willing to pay for a product. To set the price for the product, the company conducts market research and analyzes the prices for similar offers. Then the company determines the profit margin or the amount of profit it aims to gain from a product or service. After setting the profit margin, the business evaluates whether the cost of manufacturing the product is within the budget.
This strategy can guarantee that the company gets reasonable profit as the business sells the product at a price that corresponds to market demand. Large companies like automobile manufacturers choose target pricing strategy as it is not related to product demand as they sell the complete stock volume. Furthermore, target pricing increases the profitability of the companies by lowering the cost of manufacturing the product while the selling price is fixed and determined beforehand.
Toyota uses target pricing to save costs at the development stage and increases the quality of the products at the same time. The goal of the company is manufacturing costs reduction, so Toyota strives to meet the goal through design adjustments of the vehicles.
Discount (or low-cost) pricing strategy
Discount pricing strategy is a method of reducing the prices for original products or services to increase traffic, move inventory and generate additional sales. Discount pricing creates a sense of urgency and a feeling that a customer is making a good deal, so this approach attracts many potential buyers. However, a discount pricing strategy is used very often by various brands and may create a reputation that your company is a bargain retailer. In addition, it may lead to a negative perception of your products’ quality. Discount pricing strategy, which is based on cost advantage can also be used as a barrier to entry for new businesses, coming to the market.
There are three common types of discount pricing: seasonal, clearance, and volume discounts. During the seasonal discounts, companies usually provide special discounts on seasonal products. Sometimes businesses apply seasonal discounts to out-of-season products to sell old inventory. Companies use the term “clearance” to denote that the products are available at exceptionally low prices and only for a limited time, like “buy two items and get one for free”. A volume discount is also known as bundling or selling goods in bulk.
Beardbrand, a company that produces brand care products, promotes discounted bundles of its goods. The bundles are different kinds of one product. They are less expensive if purchased as a set than purchased separately. Customers can test different product variations to choose the most favorite one.
Seasonal pricing strategy
The seasonal pricing strategy sets the prices for the products depending on the demand during the high season or low season. The goal is to balance the demand by attracting customers with low prices during less busy times and increasing income in peak periods by charging higher prices. The peak seasons typically include annual holiday periods like New Year and Christmas, public holidays, school holidays, and local events like festivals and concerts.
To implement the strategy, you need to adapt to fluctuations in customer demand by breaking the year into low, mid, and peak periods. Then, determine the minimum and maximum prices you are going to charge. Try different prices to ensure that seasonal discounts do not motivate people to wait until the end of the peak period. Thus, the extra fees would not drive away customers seeking greater value.
Hotels, online travel agencies, and booking systems like Airbnb and Booking.com adjust their pricing to meet consumer demands. In addition, some services utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to determine seasonal prices with the help of the algorithm.
Psychological pricing strategy
Psychological pricing aims to create a positive psychological impact to increase sales. According to psychological studies, when customers make purchases, they experience pain or loss. Therefore, the sellers can reduce this effect, improving the chances that the customers will buy the product.
The companies employ psychological pricing strategy by setting prices ending in 9, such as $8.99 instead of $9. It looks like the seller reduced the price as much as possible, taking into account every cent. As a result, the customer perceives the price as if purchasing the product for $8 instead of $9.

Another way to use this strategy is to put more expensive items right next to the ones you are trying to sell in a physical shop or online. For example, suppose you use it in combination with discount pricing and offer a 50% discount when buying two products. In that case, customers will consider this a favorable situation to buy a product.
McDonald's uses psychological pricing by selling combination meals that seem like a good deal compared to purchasing a single product. The brand encourages people to spend money on additional products they might not otherwise buy.
Geographic pricing strategy
Geographic pricing is when a company sets different prices on its products or services depending on the market or geographical location. This strategy is suitable for multinational companies. The price for the product may be based on customers’ disposable income or the economic conditions of a particular country.
Paid social media advertising makes it simple to market a product or service using a geographic pricing strategy. You can create your pricing model focusing on the city, region, or zip code of your target customers. If some clients travel and relocate permanently, it will not influence your overall strategy to a large extent.
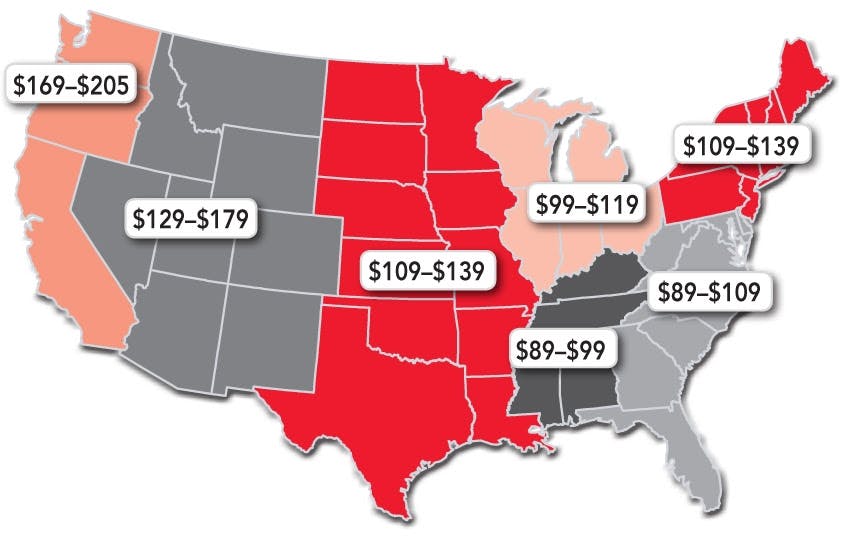
In 2019 Apple stores in China were selling the latest iPhones at discounts. Apple faces many challenges in the Chinese market as there are low-cost phone manufacturers like Huawei. Due to these obstacles, geographical pricing strategy allows the brand to compete effectively.
Map pricing strategy
Although MAP pricing might seem like a variation of the geographic pricing strategy, it is, in fact, something completely different. MAP is an acronym for Minimum Advertised Price. Some countries, for example, the United States, allow brands or manufacturers to establish MAP policies to define the lowest prices at which the retailers can promote their products. A MAP policy is a document that prevents price erosion which typically leads to lower seller margins and reduced value of the goods. In addition, MAP policy allows for identifying fraud and protects customers from purchasing fake goods. The minimum advertised price policy also specifies the consequences for companies that violate the established rules as well as the procedure for enforcing the policy.
There are MAP regulations for almost every product in the world. The policy is helpful for both manufacturers and retailers as it allows standardizing the prices and differentiating the product from the competition by focusing on its unique features like service and customer support. In addition, it helps small and mid-sized retailers compete against larger companies.
If a backpack manufacturer establishes a minimum advertised price of $50 for the best-selling item, all product resellers should advertise this product at $50 or more. However, if a reseller decides to promote the item at a $35 price, this will violate MAP regulations.
How to create a pricing strategy?
It might be challenging to develop a successful pricing strategy as it requires considering various characteristics of your business. True, creating a pricing strategy is a complicated task, so we broke the process into five steps.
1. Determine your business objectives. Your goals might include increasing profitability, introducing a new product, gaining more significant market share, or reaching a new market segment. Consider what you want your company to contribute to the economy and the world.
2. Perform a comprehensive market pricing analysis. Analyze the market in which your product or service is going to compete. If the market is over-saturated and you have many competitors offering similar products or services, the price will be your key to success. Try to reduce operational costs to maximize profit margins. If you produce a highly differentiated product, you can use premium pricing and focus on better customer service.
3. Make a list of your competitors. Competitors’ pricing strategies have a notable impact on yours. So, you need to identify several direct competitors and analyze their pricing. Then consider the alternatives that consumers may use to solve the problem instead of your product or service. Next, study the pricing of these substitute products. Finally, develop your pricing strategy based on all of the above.
4. Understand your target customers. At this stage, you need to determine why and how your target audience will use your product or service. The most important issue is the perceived value of the product. You need to understand the task your product or service solves for the customer, how it alleviates the pains related to this task, and what benefits the customer will get by using the product.
5. Set your prices and review them regularly. Finally, set the prices for your product or products based on your goals and the data you have collected. Set lower prices if you believe in market potential and want to quickly grab a larger share of it. Or set higher prices if the product you offer is superior to the competition. And make sure to review your results and update the prices if there is an opportunity to improve your results.
Now you have a better grasp of the most common pricing strategies. You can choose the most effective one for your business from the above-listed methods and then make adjustments to create more personalized experiences for your audience. It is time to offer the customers the best price for value!
