Segmenting, targeting and positioning (STP) framework in marketing
Jul 11th, 2023

The main goal of every marketing strategy is to deliver the right message to the appropriate audience. STP framework is a great tool for achieving this objective. With this method, marketers can divide consumer groups into smaller segments and develop tailored strategies to engage the customers. STP approach allows marketers to ensure that their messaging reaches the desired consumers and motivates them to take action.
Since the STP framework emphasizes identifying a specific target audience and appealingly positioning the products, your marketing initiatives become highly personalized. As a result, your marketing mix generates a higher return on investment as you spend less on channels that your audience ignores. Furthermore, your product innovation and market research become more successful as you may ask the right people to provide comments and feedback throughout the development process.
In addition, STP marketing allows small companies to find their market niches when they typically don’t have the resources to compete with larger companies in their industry. In this article, we will explain the concept of the STP framework, describe how to implement this method for your company, and provide examples of well-known brands that apply this approach.
What is STP marketing?
STP marketing is a consumer-focused marketing communications framework with three steps: segmenting, targeting, and positioning. According to this method, marketers identify the appropriate audiences and segments, focus on the groups that are best fit for the product, and then position the offering to reach the target segment. The strategy yields good results because it concentrates on breaking a client base into small groups, which allows for creating targeted marketing strategies to better connect with and engage the audience.
Before the STP model, marketers mainly focused on selling products without considering their target market or audience. In 1969, Philip Kotler created the STP model to find a more helpful method to reach customers in large and diverse markets. This strategy represents the transition from product-centered marketing to a consumer-focused approach. As a result, a more targeted and personalized approach enabled businesses to gain a better understanding of their potential buyers and how to connect with them.
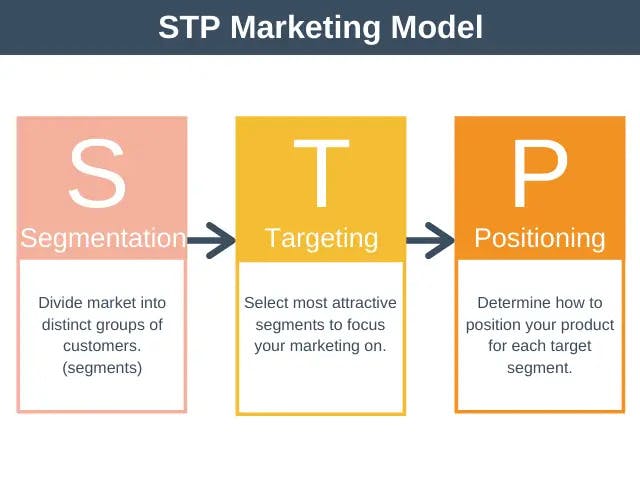
Nowadays, many marketers use the STP approach that prioritizes client demands over products. With this strategy, marketing specialists can better determine customer needs and problems and consequently increase conversion rates. Using the STP model, your company may establish a stronger presence in a target market.
The goal of the STP approach is to put the customer first. Otherwise, marketing initiatives would be too generic and uninteresting to consumers. STP provides a reliable formula for understanding customer problems and meeting their needs. Let us consider this formula in greater depth.
Segmenting
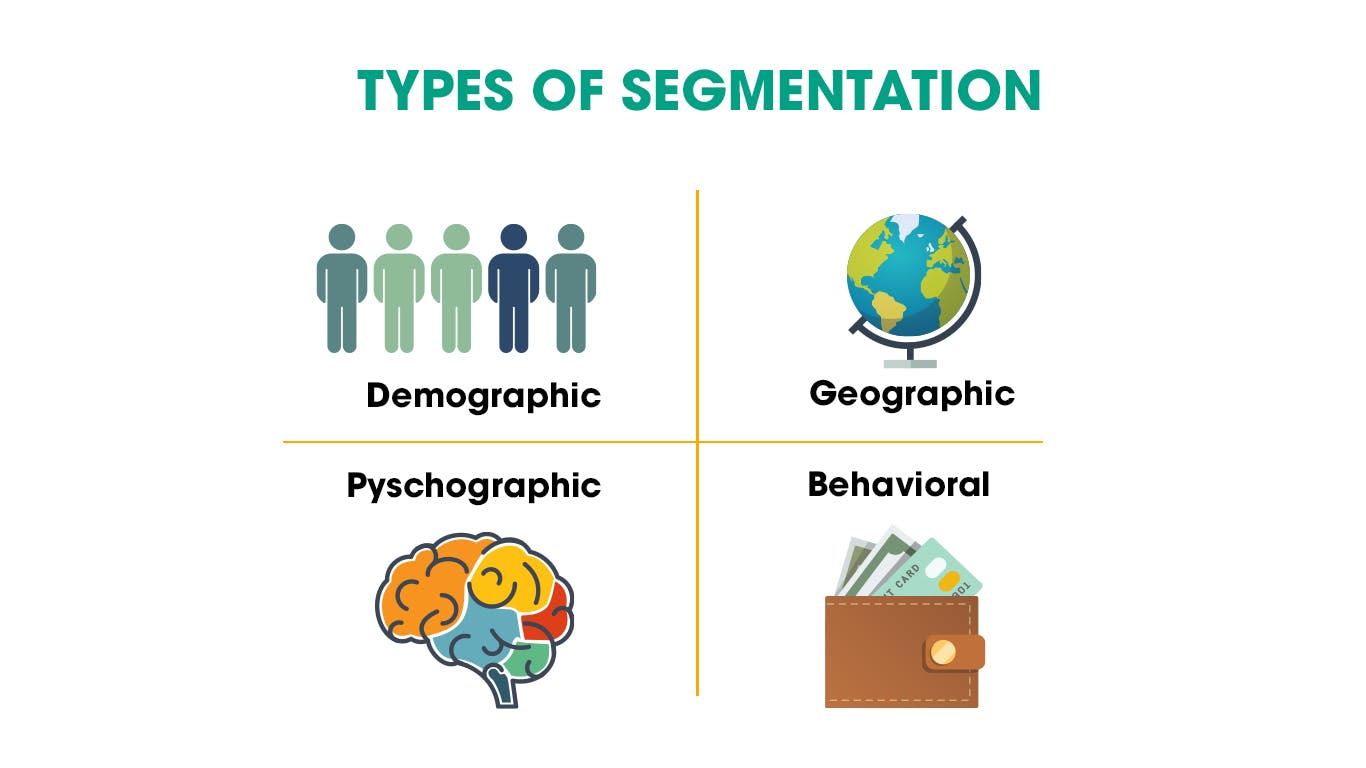
Segmenting is the first stage of STP marketing which involves identifying different customer groups that share a similar set of needs. There are four primary types of audience segmentation: geographic, demographic, behavioral, and psychographic. You can create multiple segments using these approaches. Some businesses combine demographics and geographic segmentation to develop even better descriptions of their customers.
Geographic segmentation divides your audience according to their location, such as by state or region. Demographic segmentation takes into account the audience’s age, gender, job, or education. Behavioral segmentation focuses on how consumers engage with your company: what products they buy or how frequently they make purchases. Psychographic segmentation considers lifestyle, hobbies, and activities.
Segmentation is similar to creating buyer personas, as both methods can help you identify the key characteristics of your target audience. However, using buyer personas, you can create a small number of customer profiles that reflect your larger audience. In contrast, segmentation enables you to divide your audience into several groups, each of which you may target differently.
Targeting
The second stage of the STP model is targeting. Now your objective is to analyze the segments and identify which will most likely convert into customers. A segment with strong growth, high profitability, and low acquisition cost is ideal.
Therefore, first, you need to consider the size of the segments and estimate their growth potential. The following step is to evaluate profitability. Consider which of your segments are most willing to pay for your products and services. Then calculate the customer lifetime value for each category. Take into account the reachability or how difficult it will be for you to market to each group. Finally, calculate customer acquisition costs for each segment. If it is high, this will result in low profitability.
To appropriately target a certain audience segment, you must put in a lot of effort. Concentrating on one niche market at a time is crucial, even if you identified ten. Focusing on one segment will enable you to better position your marketing for that particular group.
Positioning
The final step of the STP framework is positioning. It entails developing unique messaging for the segment you’ve decided to target. Positioning allows you to distinguish your products and services from competitors in the minds of your target market. The goal is to establish an emotional connection with the audience and encourage customers to purchase. Once you've identified your target market, you must develop a perfect combination of marketing initiatives to convert consumers into clients.
You need to examine your brand from the customers’ perspective to create a strong product positioning. Think why potential buyers would choose your product or service over similar offerings. Consider features and benefits that are relevant to your audience. Identify their motivations and pain points. Analyze existing customers’ comments and feedback to produce content that resonates with your audience.
You can consider three types of positioning to stand out from the competition: symbolic positioning, functional positioning, and experiential positioning. Symbolic positioning or lifestyle positioning addresses self-image enhancement and social meaningfulness. Functional positioning solves customer problems and provides unique advantages. Experiential positioning focuses on the emotions and experiences your product or brand offers customers.
Effective positioning combines all three elements. In the next section of this article, we will discuss how to create an STP marketing framework for your business.
How to develop an STP marketing framework?
We outlined the three STP marketing framework stages to provide you with an understanding of the concept. Now we will delve into the specifics of developing an STP marketing plan that benefits your company.
Step 1. Determine the market
Before segmenting the market for your personal needs, it is crucial to divide the global market into smaller sections and determine the ones to focus on. You can start by determining TAM, SAM, and SOM. Let us consider each of these terms in more detail.
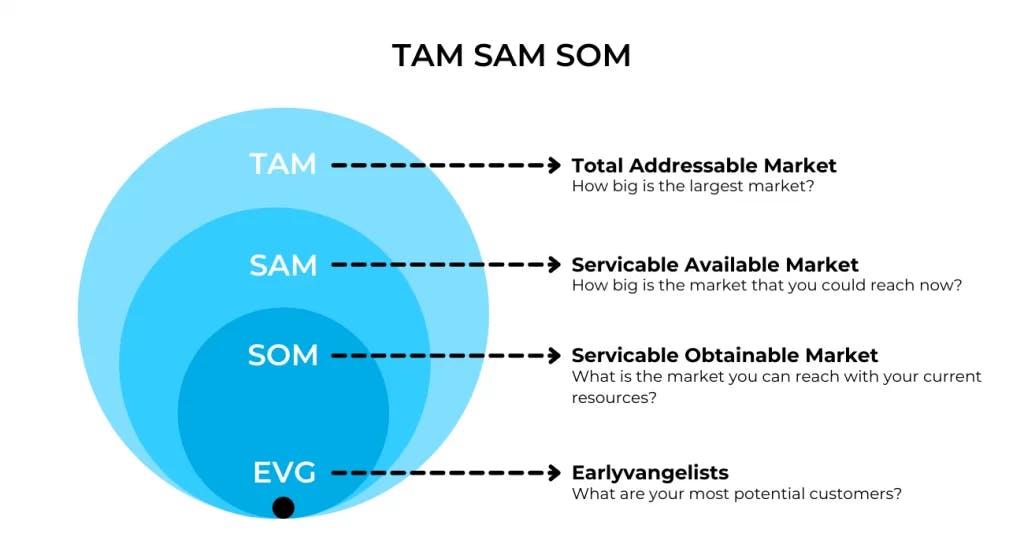
TAM, or Total Addressable Market, is the general need for an offering on the market or the largest available market for the brand. It is the amount of money a company can make if it controls 100% of the market.
SAM or Serviceable Available Market is a part of the entire market that is suitable for the offering. You can identify SAM by geographical or product-specific limitations.
SOM or Serviceable Obtainable Market is a part of SAM a company can address after taking into account aspects like funding, product differentiation, and competitors.
Step 2. Segment the market
Once you have determined the SAM, you can divide the customers into segments based on geography, demography, behavior, or psychography. A combination of all four will enable you to create components that are different from one another. You will get more clearly defined segments if you add more segmentation layers and attributes, including age, gender, location, and income. These factors help you determine the marketing channels and audiences where your initiatives provide the highest ROI.
For example, you have divided your SAM into men and women based on demographics. Then you need to consider more segmentation factors to identify a specific audience. Perhaps you target women living in Ireland (demographics) who tend to buy high-end goods (psychographics). These people follow your company on social networks and already visited your website (behavior).
Thus, using layers and variables allows you to tailor your marketing activities to each specific customer group and create a highly personalized experience. According to research by McKinsey, businesses that succeed in personalization earn 40% more revenue than average businesses.
Step 3. Examine the segments
At this stage, you need to estimate the profitability of each segment. To complete this task, you should conduct primary customer research or use available market data. When evaluating the segments, consider the following factors: growth rate, size of the segment, return on investment, price sensitivity, brand loyalty, buying power, and rivals that market to that group. With this knowledge, you'll be able to assess the profitability of each segment.
Then you can create segment profiles. These in-depth descriptions of people in each group are very similar to ideal buyer personas. Describe their demands, habits, demographics, brand preferences, behaviors, and other factors. It will help you better understand potential buyers within each group.
Step 4. Identify target audiences
Once you have collected detailed information about your customers, it is time to decide which ones are the most suitable for your product or service. You need to consider the organization’s strategy, the attractiveness of the category, and the level of competition in that market. In addition, you can use cluster analysis to define the most viable segment.
Your ideal target segment should be reachable, large, and expanding. It is crucial to focus on a target segment that matches your company’s capabilities. Therefore, you need to evaluate the number of products the company can produce and where it can send them. Moreover, performing a SWOT analysis, finding gaps, and accessing competitors’ capabilities is critical.
Step 5. Develop positioning strategy
Now it is time to create your positioning strategy. This stage focuses on the prospective customers’ perception of a product or service compared to other offerings available on the market. There are several types of positioning you may follow. We will describe each of them below.

Rival-based positioning emphasizes the features of your offering that are better than rival offerings. Customer-based positioning focuses on consumer demands and how your product satisfies them. Advantage-based positioning highlights the benefits that your clients will get from buying your offering. Price-based positioning demonstrates the value consumers receive when purchasing a product. Feature-based positioning concentrates on your value proposition that makes your offering unique. Prestige-based positioning accentuates higher product quality and impact on reputation or status.
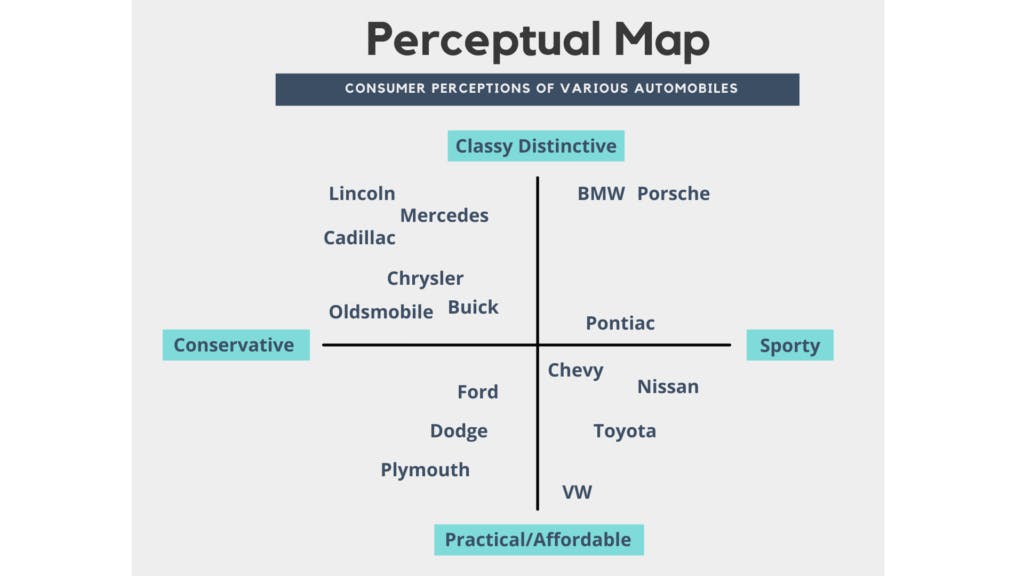
To create a successful positioning strategy, you need to draw a perceptual map. Using a visual representation, this method can help you compare your product to rivals’ offerings. You may understand where your product stands against competitors by using two market attributes crucial for your target markets, such as quality and price.
Step 6. Define a marketing mix
The final stage of the STP approach is to create your marketing mix, which includes product, price, place, and promotion. The product covers the attributes like superiority over the competition, features, advantages, quality, design, packaging, and convenience.
Price reflects aspects like pricing strategy, discounts, and payment methods. Keep in mind that pricing your products substantially lower than your competitors may benefit you right away but would negatively impact your sales in the long term.
Place refers to the locations where customers can purchase your product, like physical and online stores. It also includes inventory, logistics, and distribution channels.
Promotion considers how your offering reaches customers. It encompasses advertising campaigns, word-of-mouth, influencer marketing, and other strategies.
A perfect marketing mix leads to business success. However, if you miss any elements, all the hard effort you put into the earlier phases can be for nothing.
Examples of STP marketing
Now we will consider some examples of well-known brands that use STP marketing to attract and engage clients. We will make a detailed analysis of each brand’s segmentation, targeting, and positioning.
Apple
Apple’s demographic segmentation covers four major customer groups: teenagers, college and university students, business people, and adults. Teenagers mostly use iPads to listen to music, watch movies and make video calls. Students use iPads and MacBooks to make notes. Additionally, the lightweight design of these gadgets makes them convenient for carrying to college. Business people and professionals prefer iPads, iPhones, and MacBooks because of the innovative design, software, and features they need for their jobs. Adults choose iPhones because of the built-in navigation map, high-quality camera, and FaceTime for video calls.
Since Apple is a premium brand and is typically found in metropolitan areas with affluent consumers who can afford to buy high-end products, lifestyle is the most crucial factor among the segmentation criteria.
Apple’s target market is well-off consumers ready to pay more for technology products with cutting-edge functionality and design. After years of analysis, the company found that the majority of consumers appreciate the products’ quality, performance, and design over pricing.
The company uses competitor-based and prestige-based positioning strategies. Apple positions itself as a luxury brand that appeals to entrepreneurs, businesspeople, and high-earners. Since there is fierce rivalry in the technology sector, Apple continuously invests in R&D and develops exclusive technologies for the brand that competitors are unable to fully copy.
McDonald’s
McDonald’s divides its consumers into the following geographical segments: the US, Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. The company takes into account the tastes and needs of customers from different countries and optimizes the menu accordingly. For example, Indian consumers can buy McAloo Tikki and McVeggie, and US customers can try Bacon Smokehouse Burger and Quarter Pounder Burger.
According to demographics, McDonald’s specifies three groups of consumers: children, young people aged 18-29, and adults. To draw in a younger population, McDonald's offers a variety of toys, happy meals, and other offerings. The company also added healthier food options like salads, apple slices, and oatmeal to attract adults.
McDonald’s main target customers are people seeking quick, convenient, affordable meals. By adding new menu items and technologies, such as smartphone ordering and self-service kiosks, the corporation has also been focusing on millennials and young people. In addition, the company has been advertising its morning menu to commuters and other busy individuals.
McDonald’s positions itself as a family-friendly, affordable restaurant that offers high-quality food and drinks. The firm's marketing initiatives strongly emphasize high-quality ingredients and customer satisfaction. McDonald's also promotes itself as an innovator by offering new menu items and technologies to improve the consumer experience. For instance, the business released a mobile ordering and payment application that enables users to order and pay for meals using smartphones.
Nike
Nike categorizes its products according to demographic characteristics like gender and age groups. The company offers sports clothing and footwear for men, women, and teenagers between 15 and 55 years. Geographic segmentation covers the US, Europe, Australia, Asia, and Africa. Nike examines the national characteristics of customers from different countries and uses these features to create advertising campaigns. For example, most Nike commercials in the US focus on football and baseball, while European advertisements demonstrate soccer. The company also promotes equipment for rugby and cricket in England.
The company primarily targets athletes and sports enthusiasts who follow a healthy lifestyle and practice fitness activities. However, the targeting also focuses on people who prefer fashionable clothes and affluent customers. Nike creates footwear for men suitable for athletics, baseball, basketball, tennis, and other sports. Besides this, Nike offers women's yoga shoes in their line of footwear.
Nike’s unique selling proposition, which has helped the company build a long-lasting competitive edge, is high-quality, comfortable products for all athletic categories. Customers who want to express their individuality will find the NikeID line interesting because it offers the option to personalize shoes and other accessories.
Nike has positioned its brand as the industry leader in high-quality sporting goods with innovative technology. Company’s logo and “Just Do It” slogan promote the outstanding accomplishments of famous athletes. The brand is associated with top worldwide sports teams and events and represents achievement and personal growth.
The STP approach is a valuable technique for digital marketers that allows them to create target audiences for different marketing initiatives, both for traditional and digital marketing campaigns. With this framework, you can find the most profitable markets, position your products and meet customer demands. STP model will help you identify new clients, experiment with different target audiences and achieve outstanding results.
